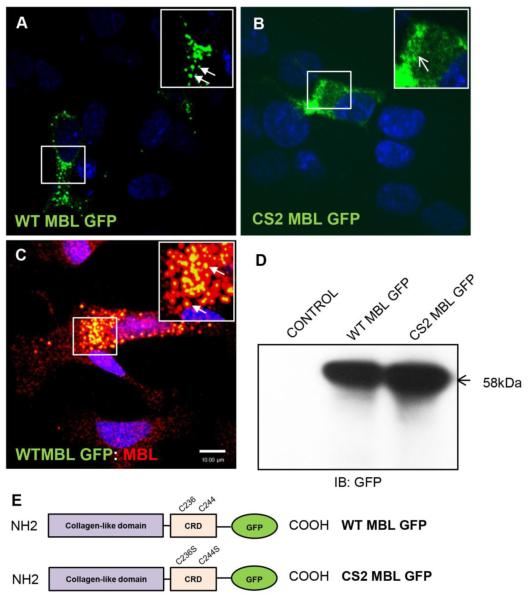
Figure 1. Subcellular localization of neuronal MBL at perinuclear vesicles requires functional carbohydrate recognition domain.
A, B, C, Confocal laser scanning microscopy analysis of SK-N-SH cells transfected with WT MBL-EGFP (A) or CS2 MBL-EGFP plasmid (B) or simultaneous expressing endogenous MBL and exogenously transfected WT MBL-EGFP (C). A, WT MBL-EGFP is localized at perinuclear vesicles (closed arrows). B, CS2 MBL-EGFP is diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm (open arrows). C, Functional co-localization of endogenous MBL with exogenously expressed WT MBL-EGFP (closed arrows, yellow indicates co-localization). SK-N-SH cells were immunostained for endogenous MBL (red) followed by corresponding Alexa Fluor secondary antibodies. GFP (green) was observed by its own fluorescence. DAPI (blue) stained nuclei. D, Western blot analysis of untransfected control cells and WT and CS2 MBL-EGFP expressing SK-N-SH cell lysates. E, Schematic representation of the domain structures of WT MBL-EGFP and CS2 MBL-EGFP: Collagen-Like Domain; Carbohydrate Recognition Domain (CRD). The two cysteine residues C236 and C244 in CRD domain were subjected to mutagenesis (WT MBL-EGFP panel). Double point mutation is displayed in the CRD of MBL as C236S and C244S (CS2 MBL-EGFP panel). Scale bar, 10 μm.