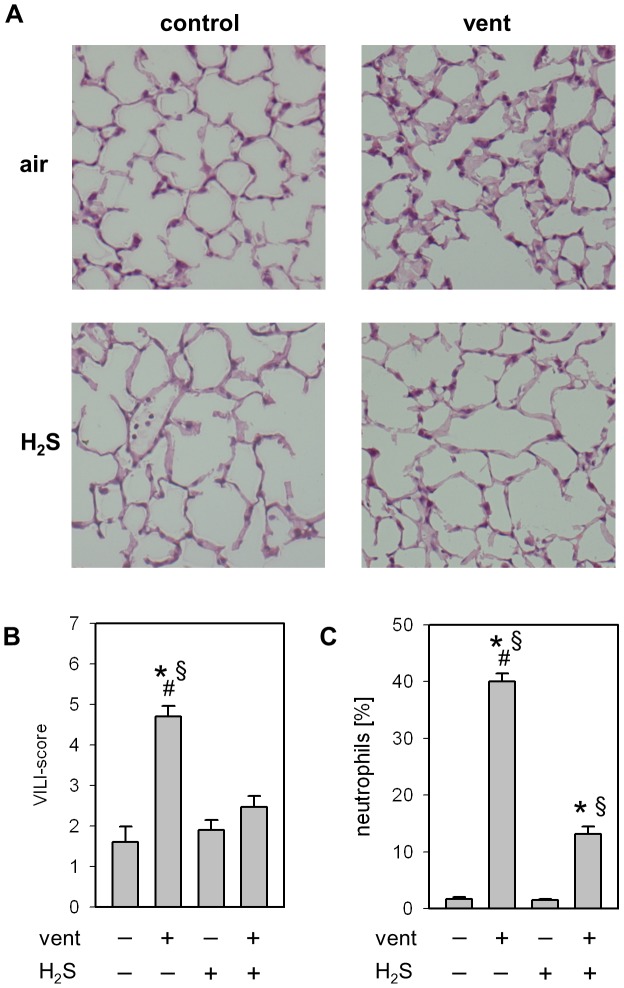
Figure 1. Effect of ventilation and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) treatment on lung injury.
(A) Representative pictures of H&E stained lung tissue from animals mechanically ventilated (vent)(12 ml/kg, 6 h) in the absence or presence of supplemental H2S (80 ppm) and their corresponding non-ventilated controls. (B) Ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) score was measured from the histology samples and (C) the relative amount of neutrophils was determined by cytospin analysis of BALF. Data represent means ±SEM for n = 5/group. Analysis of variance (Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test), *P<0.05 vs. control; #P<0.05 vs. H2S control; §P<0.05 vs. H2S-ventilated group.