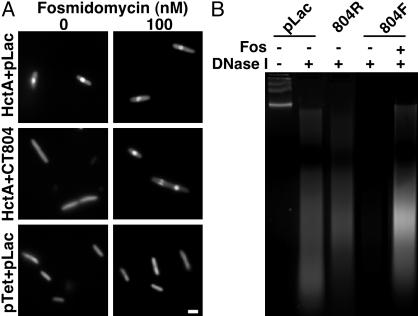
Fig. 4.
(A) Acridine orange staining of E. coli induced to express Hc1 (HctA + pLac), Hc1 and CT804 (HctA + CT804), or parent vectors only (pTet + pLac), in the absence or presence of 100 nM fosmidomycin. Condensed DNA appears as a central brightly fluorescent sphere (10). (Bar equals 1 μm.) (B) DNase I digestion of C. trachomatis L2 EB nucleoids incubated with deproteinated extracts of E. coli cultures expressing the parent plasmid, pLac; CT804 in a nonexpressing reverse orientation (804R), CT804 in an expressing orientation (804F), or CT804 in an expressing orientation in the presence of fosmidomycin (Fos). Untreated chlamydial chromosomal DNA from EB nucleoids runs as a high molecular weight band or bands. Chlamydial chromatin associated with Hc1 is partially protected from DNase I digestion such that it is nicked and appears as a ladder or smear on the gel. When Hc1 is dissociated, the DNA is exposed and completely digested.