Figure 5.
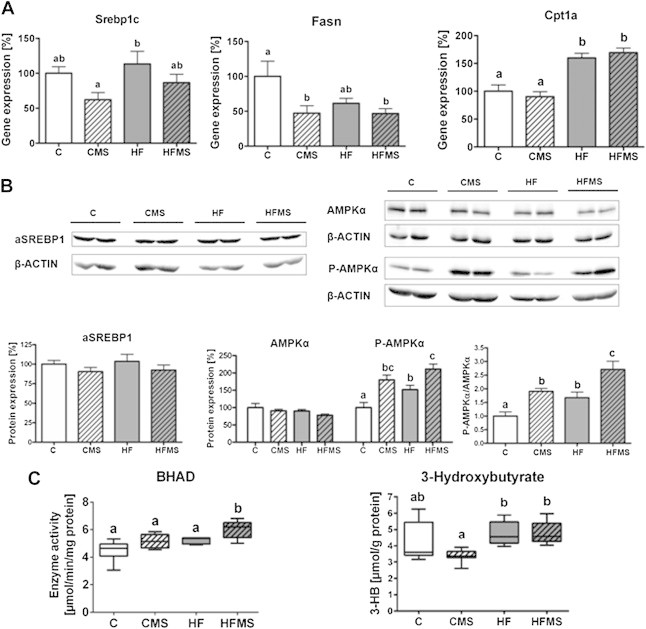
Influence of 4-weeks dietary methyl-donor supplementation on de novo lipogenesis, pivotal regulators, specific enzyme activity of fatty acid oxidation and ketone body production in the liver. (A) Gene expression of Srebp1c, Fasn and Cpt1a. (B) Protein expression of activated SREBP1 (aSREBP1), and AMPKα expression (AMPKα) and phosphorylation (P-AMPKα). (C) β-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase (BHAD) enzyme activity and 3-hydroxybutyrate concentrations. Separate gels were run for quantification of total AMPKα and P-AMPKα. β-ACTIN of the respective membranes were used for protein normalization. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5–9). Open, gray, open lined and gray lined boxes show data from C, HF, CMS and HFMS animals, respectively. Different subscript letters indicate statistical significance (p < 0.05). 3-HB, 3-hydroxybutyrate; AMPKα, AMP-activated protein kinase α; P-AMPKα, phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α (Thr172); aSREBP1, soluble activated SREBP1; β-HAD, β-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase; Cpt1a, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a; Fasn, fatty acid synthase.
