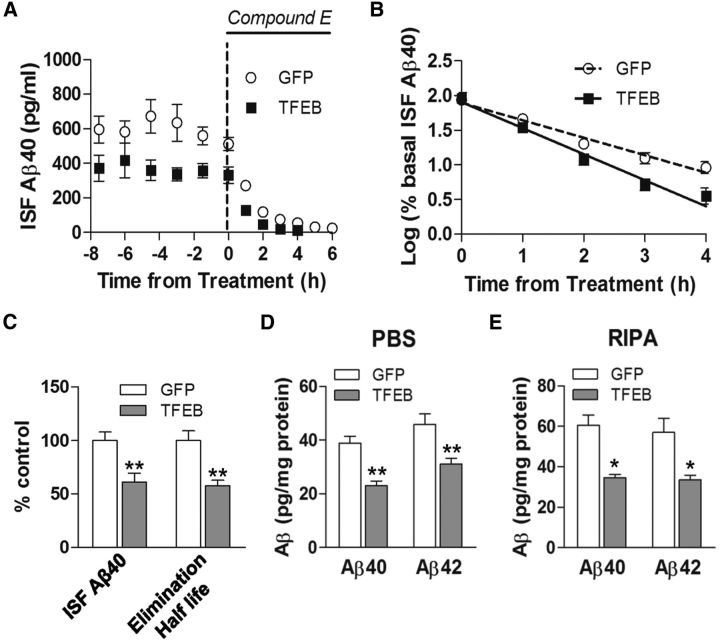
Figure 6.
AAV8-mediated astrocytic gene transfer of TFEB reduces brain ISF Aβ levels and reduces in vivo Aβ half-life. A, Assessment of Aβ levels by in vivo microdialysis in 3-month-old APP/PS1 mice transduced with AAV8-GFAP-FLAG-TFEB (TFEB) and AAV8-GFAP-eGFP (GFP) with serial hourly measurements. N = 5 mice/group. At t = 0, mice were continually administered Compound E directly to the hippocampus (200 nm, reverse microdialysis) followed by hourly sampling for Aβ. Mean absolute in vivo “exchangeable” Aβ (eAβx-40) concentration was averaged over a 9 h period before drug administration, and assessed to be 362.4 ± 49.0 pg/ml in TFEB-transduced mice versus 592.5 ± 46.9 pg/ml in controls. B, Semi-log plot of decline in percentage basal ISF Aβ levels during administration of Compound E, in animals in A. Half-life in control mice was 1.26 ± 0.11 h and 0.76 ± 0.06 h in TFEB-expressing mice. C, Quantification of averaged concentration and elimination half-life of ISF Aβ as calculated in A and B; **p < 0.01. D, E, Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in dissected hippocampal tissues from AAV8-GFAP-FLAG-TFEB (TFEB) and AAV8-GFAP-eGFP (GFP) transduced APP/PS1 mice (5 months of age). Tissue was homogenized first in PBS (D) and then in RIPA (E) quantified with ELISA assay. HJ2 and HJ7.4 antibodies were used for capture Aβ40 and Aβ42, respectively, and HJ5.1 antibody was used for detection. N = 5 mice/group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.