Figure 4.
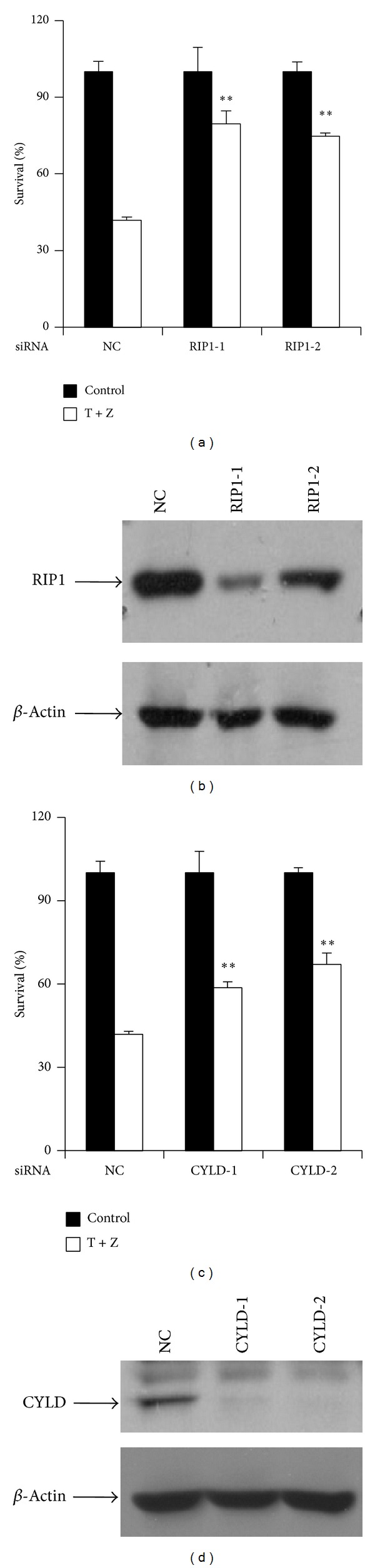
RIP1 and its deubiquitinase CYLD are required for TNF-α-induced necrosis of HT-22 cells. (a) HT-22 cells were transfected with the negative control or RIP1 siRNAs. After 60 h, cells were treated with control or TNF-α/z-VAD for another 20 h and then cell viability was determined by measuring ATP levels. Data were represented as mean ± standard deviation of duplicates. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001 versus NC-T + Z. (b) The knockdown efficiency of RIP1 RNAi. Cell lysates were collected 60 h after transfection and subjected to western blot analysis of RIP1 and β-actin levels. (c) HT-22 cells were transfected with the negative control or CYLD siRNAs. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were treated with control or TNF-α/z-VAD for another 20 h and then cell viability was determined by measuring ATP levels. Data were represented as mean ± standard deviation of duplicates. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001 versus NC-T + Z. (d) The knockdown efficiency of CYLD RNAi. Cell lysates were collected 60 h after transfection and subjected to western blot analysis of CYLD and β-actin levels. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
