Figure 3. Contribution of FcγRIII mechanism in mediating albumin nanoparticle internalization.
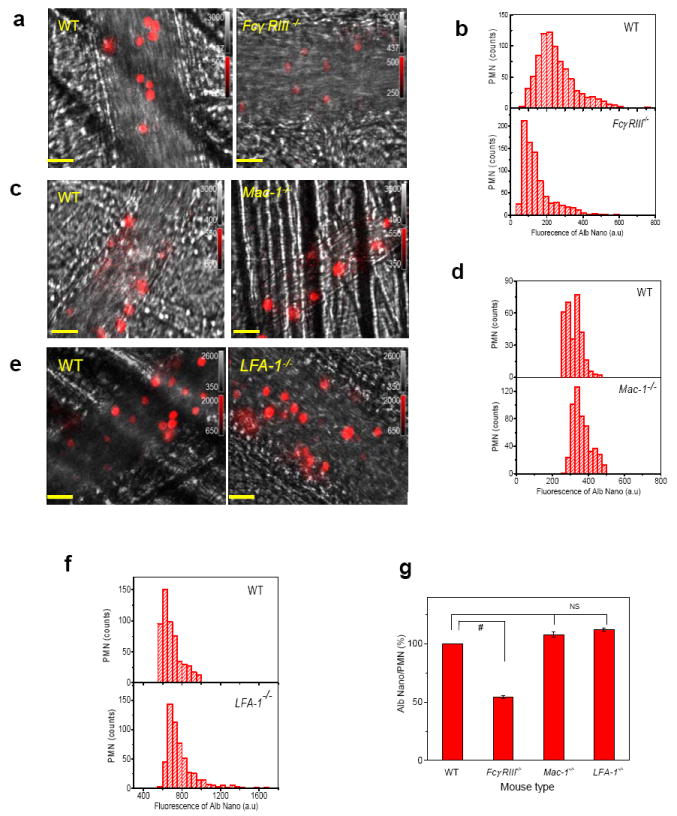
a-f, Intravital microscopy of cremaster muscle inflamed venules was performed in wild-type (WT) and FcγRIII-/- (a), Mac-1-/- (c), and LFA-1-/- mice (e). Scale bars, 20 μm. Cy5-loaded albumin nanoparticles (red) were intravenously infused 3 hr after the intrascrotal injection of TNF-α (0.5 μg/mouse). Histograms of Cy5-loaded albumin nanoparticles internalized by neutrophils in WT and FcγRIII-/- (b), Mac-1-/- (d), and LFA-1-/- mice (f) were obtained from more than 500 neutrophils in 3 mice per group. Integrated fluorescence intensities of nanoparticles in individual polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). g, Percentage albumin nanoparticle uptake in WT versus knockout mice in each group based on data from (b, d, and f). Results are shown as mean ± SEM. # P<0.0001 vs. WT mice after ANOVA and Dunnett’s test. NS, not significant.
