Figure 6.
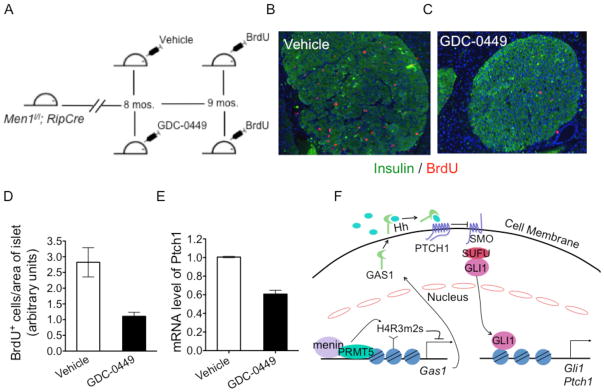
Inhibition of Hedgehog (Hh) signaling in Men1-excised mice results in decreased islet cell proliferation. (A) Scheme for inhibition of the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway with GDC-0449 in Men1-excised mice. (B–C) Immunofluorescence for BrdU and insulin in pancreas of Men1-excised mice gavaged with either vehicle (B), or GDC-0449 (C) for four weeks at a dose of 100 mg/kg b.i.d. (D) Quantitation of BrdU incorporation in islets of mice above (same as B, C). (E) Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) for Ptch1 mRNA in islets of Men1l/l;pdxCreER mice gavaged for 10 days with either vehicle or GDC-0449 at a dose of 100 mg/kg b.i.d., p = 0.0010. (F) A model for menin-PRMT5-mediated inhibition of Hh signaling through epigenetic regulation of GAS1. Error bars indicate ± s.d.
