Figure 3. OS-DC increases peptide-specific activation of CD4+ T cells.
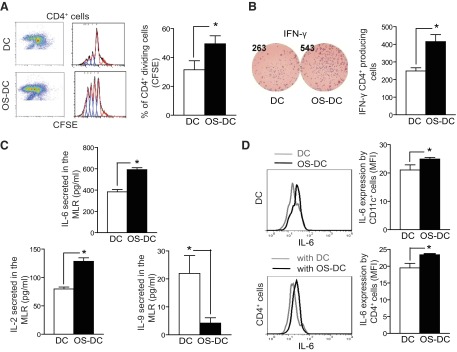
DC were incubated for 24 h in medium alone (control DC) or in the presence of 500 μM H2O2 (OS-DC). A total of 1.0 × 104 OS-DC or control DC from C57BL/6 mice was pretreated with OVA-II peptide and cocultured in a MLR with 1.0 × 105 OVA-specific CD4+ cells (isolated from OT-II spleens using microbeads). (A) After 72 h, flow cytometry evaluation revealed an increase in proliferation of CFSE-labeled CD4+ T cells, cocultured with OS-DC, compared with those cocultured with control DC (*P=0.005; n=4 each group). (B) With the use of the ELISPOT assay, IFN-γ was assessed after 24 h of coculturing; an increase in IFN-γ secretion was noted when CD4+ T cells were cocultured with OS-DC compared with control DC (*P=0.009; n=4 each group). (C) After 72 h of coculturing, the supernatant was collected from the MLR, and cytokine production was measured using Luminex. An increase in IL-6 (*P<0.001) and IL-2 (*P=0.005) but a decrease in IL-9 levels (*P=0.04) was observed when CD4+ T cells were cocultured with OS-DC compared with control DC (n=4 in each group). (D) To determine the source of increased IL-6 secretion, cells were collected from the MLR after 72 h of coculturing and stimulated with PMA and ionomycin in the presence of monensin. Cells were then labeled with surface staining for CD11c and CD4 and with intracellular staining for IL-6. An increase in IL-6 secretion, as measured by MFI, was observed in OS-DC compared with control DC (*P=0.05, n=3). Similarly, an increase in IL-6 secretion, as measured by MFI, was observed in CD4+ cells that were cocultured with OS-DC compared with those cocultured with control DC (*P=0.04, n=3).
