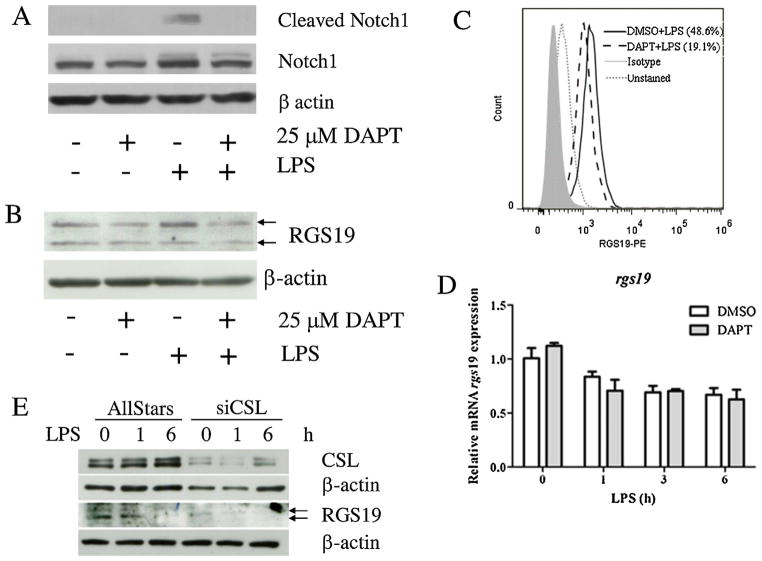
Fig. 2.
Effect of DAPT treatment on RGS19 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. (A) The RAW264.7 cell line was pretreated with DAPT (25 μM) for 1 h before stimulation with 100 ng/ml LPS for 1 h. Cleaved (Val1744) and total Notch1 were detected using Western blotting, and β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) Protein lysates were collected to investigate the presence of RGS19 by Western blotting, as described above. Arrows indicated the two bands corresponding to phosphor-RGS19 and total RGS19. (C) The RAW264.7 cell line was treated as indicated, harvested and stained with anti-RGS19 antibody. The level of RGS19 was detected using flow cytometry. (D) The mRNA levels of rgs19 were measured using qPCR. Total RNA was harvested from LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells after treatment with DAPT or DMSO for 0, 1, 3 and 6 h after LPS stimulation. (E) The RAW264.7 cell line was transfected with a control scramble siRNA or CSL-specific siRNA and subjected to LPS stimulation. The expression of RGS19 and CSL were detected by Western blotting.