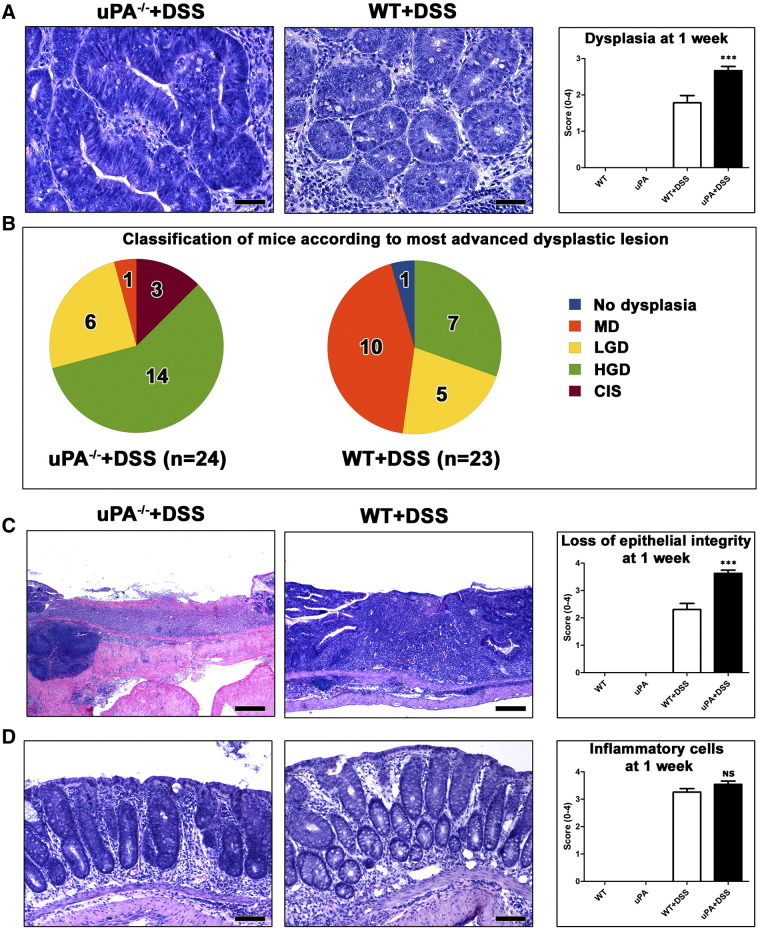
Figure 3.
Effects of uPA deficiency in the histopathology of colitis at 1 week after DSS treatment. (A) CIS arising in glands with HGD in uPA−/− + DSS mouse colitis. Typical LGD from a WT + DSS mouse is shown on the side for comparison. Colitis-associated dysplasia scores are significantly raised due to deficiency in uPA. (B) The occurrence of the most advanced grades of dysplasia is higher in uPA−/− mice compared to their WT counterparts. (C) The healing of typical DSS-induced colonic ulcers is retarded due to uPA deficiency. Consequently, the surface epithelium deficit scores are significantly higher in uPA−/− than in WT mice. (D) In non-ulcerated areas of colonic mucosa, uPA−/− and WT mice show comparable amounts of inflammatory cell infiltration. Hematoxylin and eosin (A, C, and D). Scale bars, 50 μm (A); 250 μm (C); 100 μm (D). Numbers on the y-axis of bar graphs correspond to the means ± SEM of histologic scores; ***P < .0001; NS, P > .05.