Table 1.
Examples of different MT primary structure from unconventional species. In the first line human (Homo sapiens) MT-2A is reported for comparison. Cysteines are evidenced in yellow, lysines in green and histidine in red. Histidine has been evidenced because of its possible involvement in metal binding. Cys: cysteine; AA: aminoacid. The sequences are referred to dolphin (Tursiops truncatus), cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo), lizard (Podarcis sicula), newt (Triturus carnifex), goldfish (Carassius auratus), sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus), mussel (Mytilus edulis), arcid clam (Scapharca inaequivalvis), snail (Helix pomatia), blue crab (Callinectes sapidus), common fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster), polychaete (Perinereis nuntia), earthworm (Lumbricus rubellus) and nematode (Caernorabditis elegans). All the sequences were obtained from GenBank. * The sequence of S. inaequivalvis MT is not complete.
| Species | Name | Sequence | Cys | AA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. sapiens | MT-SA |  |
20 | 61 |
| Vertebrates | ||||
| T. truncates | MT-2A |  |
20 | 61 |
| P. carbo | MT-2 |  |
20 | 63 |
| P. sicula | MT |  |
20 | 63 |
| T. carnifex | MT |  |
20 | 63 |
| C. auratus | MT |  |
20 | 60 |
| Invertebrates | ||||
| S. purpuratus | SpMTA | 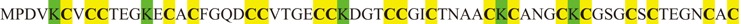 |
20 | 64 |
| M. edulis | MT10Ib |  |
21 | 73 |
| S. inaequivalvis | MT |  |
18 | 62 |
| H. pomatia | CuMT |  |
18 | 65 |
| C. sapidus | CuMT-2 |  |
21 | 64 |
| D. melanogaster | MtnE |  |
10 | 41 |
| P. nuntia | MT |  |
17 | 68 |
| L. rubellus | MT-1 |  |
20 | 79 |
| C. elegans | CeMT-1 |  |
19 | 75 |
