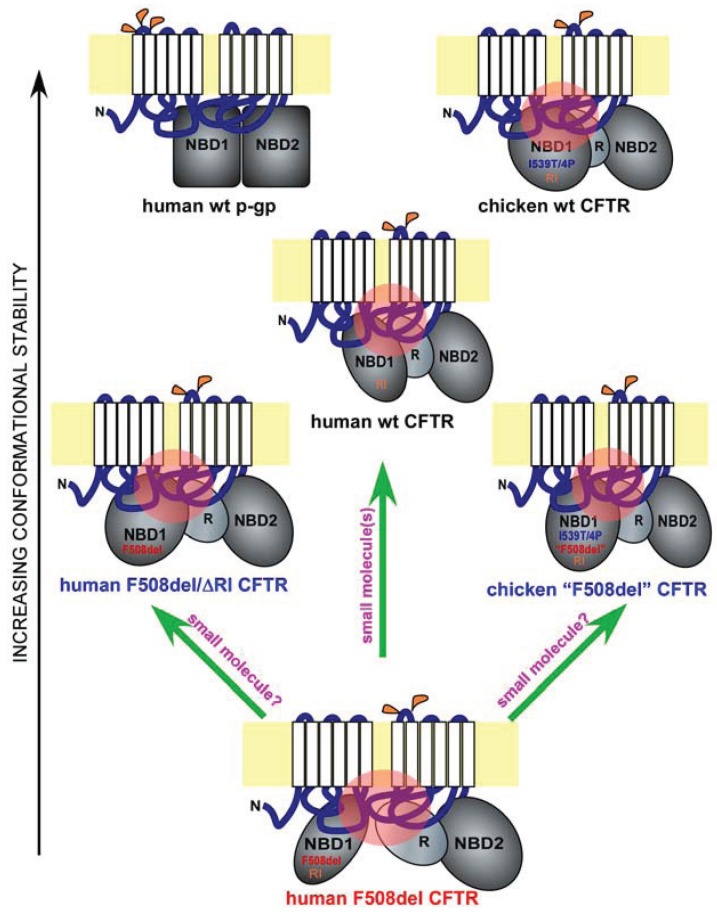
Figure 1.
Misfolding and rescue of F508del cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Shown are domain conformation of human full-length wild-type (wt) CFTR, its paralogue p-glycoprotein (p-gp), and other CFTR homologues and mutants, as indicated. In each panel, a full-length ABC protein is anchored to the membrane bilayer (in yellow) through two six-pass membrane-spanning domains (white). The extracellular and cytoplasmic loops are in blue, and the major cytoplasmic domains such as the two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2) and the regulatory domain (R) are in grey. Glycosylation sites on the extracellular loops are labeled in orange (p-gp has three and CFTR has two). The different shapes and orientations of the major cytoplasmic domains represent their different conformations. Key sequence variations in NBD1 are labeled. I539T/4P refers to the combined I539T and four proline substitutions occurring in chicken CFTR. “F508del” refers to the chicken version of the human F508del mutation. RI refers to the presence of the regulatory insertion. Key interdomain contacts for CFTR are labeled by pink circles. The proteins are arranged in the order of conformational stability. Green arrows represent potential F508del rescue strategies.