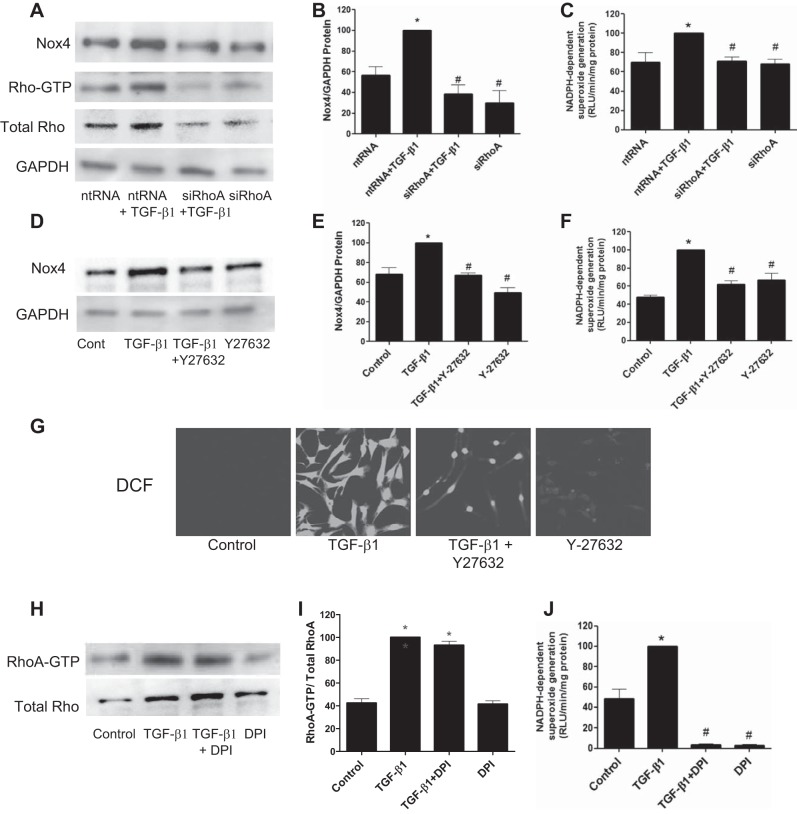
Fig. 6.
The RhoA/ROCK pathway signals Nox4-derived ROS. A and C: kidney fibroblasts were treated with siRhoA or ntRNA for 72 h followed by stimulation TGF-β1 or diluent, and Nox4 expression (A) and NADPH oxidase activity (C) were then examined 30 min later. A–C: siRhoA inhibited the TGF-β1-induced increased expression of Nox4 protein (A and B) and NADPH oxidase activity (C). D–F: similarly, cells treated with the ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 before the addition of TGF-β1 blocked the increased expression of Nox4 protein (D and E) and NADPH oxidase activity (F) relative to diluent controls. A–F: inhibitors alone had no effect on basal levels of Nox4 protein or NADPH oxidase activity. G: ROS generation, detected by 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein (DCF) fluorescence, was also inhibited by Y-27632 within 30 min after incubation with TGF-β1. H–J: inhibition of Nox4 using diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) had no effect on TGF-β1-induced activation of RhoA-GTP (H and I) but reduced NADPH oxidase activity (J), indicating that RhoA is upstream of Nox4. *P < 0.05 vs. control. #P < 0.05 vs. TGF-β1 according to ANOVA.