FIGURE 14.
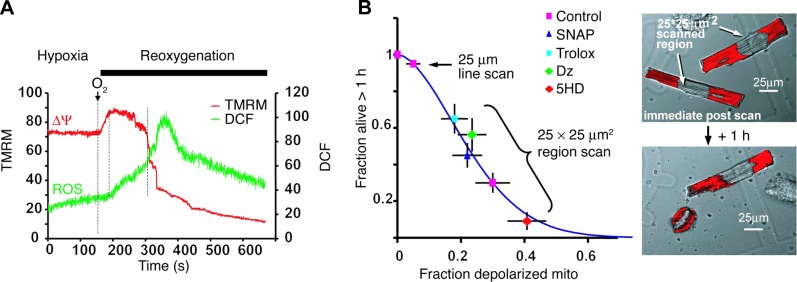
ROS are involved in mitochondria and cell deterioration. A: hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced mitochondrial hyperpolarization leads to increased ROS. Mitochondria stained with TMRM (Δψ, red) and DCF (ROS, green) were laser line-scanned (2 Hz) during hypoxia and the reoxygenation phase. The ROS burst is delayed after reoxygenation and starts at the maximum Δψ. Mitochondrial hyperpolarization lasts for ∼2 min, followed by loss of Δψ. B: cell survival after constant-energy photoexcitation of a 25 × 25 μm2 region. Right panels show TMRM-stained cardiomyocyte (red) immediately after, and 1 h after, irradiation. Survival is inversely related to the fraction of mitochondria (mito) undergoing mPTP induction and is improved by ROS scavenger (Trolox), NO donor (SNAP), and the KATP channel opener diazoxide (Dz) and is impaired by 5-hydroxydecanoate (5HD), the blocker of KATP channel. [From Juhaszova et al. (218). Republished with permission from the American Society for Clinical Investigation; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.]
