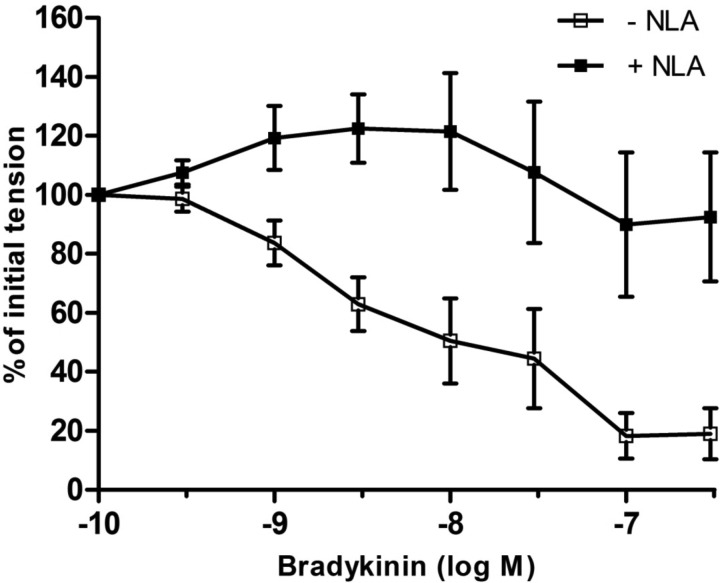
Fig. 2.
Effect of nitro-l-arginine (NLA; 3 × 10−5 M) on bradykinin-induced relaxation of isolated fetal coronary arteries from ewes fed a nutrient-restricted (60%) diet during the last ⅔ of pregnancy. Data are expressed as a percentage of the initial increase in tension induced by U46619 (3 × 10−9 M), which averaged 2.38 ± 0.2 and 2.50 ± 0.3 g in coronary arteries in the absence and presence of NLA, respectively (P > 0.05). Each point represents the mean ± SE; n = 6.