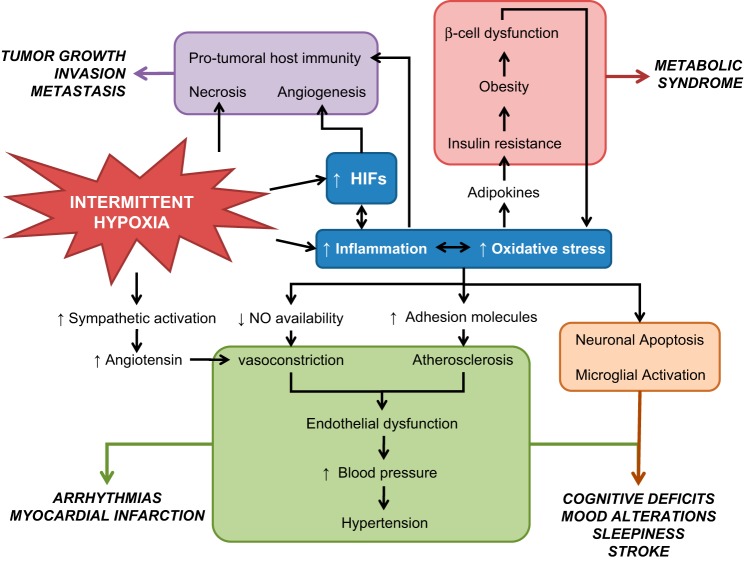
Fig. 2.
General diagram of the detrimental effects of IH on cognitive, metabolic, cardiovascular, and cancer outcomes. IH can promote oscillations of oxygen levels in the whole organism. Some tissues, concretely those that are more dependent on oxygen, could experience apoptosis during IH as occurs in some neurons or cardiomyocytes. Also, IH can induce necrosis in tumor tissues where there is a high metabolism and oxygen demand. Although the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) by intermittent hypoxia is not clear among the different studies, the recurrent oxygen oscillations can promote inflammation and/or oxidative stress, which in turn could activate HIF pathways. IH-induced chronic inflammation has been related to the majority of consequences of sleep apnea and promoting cardiovascular, metabolic, and cognitive disorders. Very recently, inflammation and oxygen oscillations have been associated to increased tumor aggressiveness. NO, nitic oxide.