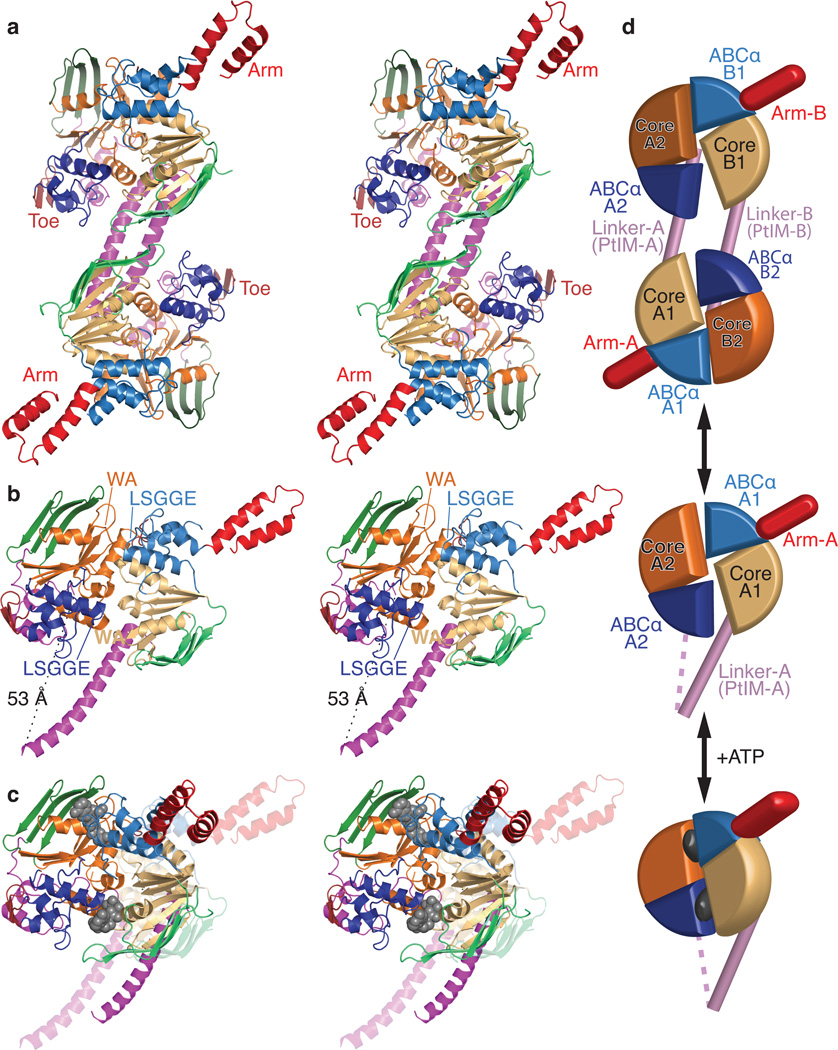
Figure 2.
Crystal structure of E. coli EttA. (a) Stereopair showing the nucleotide-free EttA dimer in the asymmetric unit (Table 1). The ABC domains in each protomer are colored lighter (ABC1) and darker (ABC2) shades of similar colors (green for ABCβ, tan-orange for F1-like core, and blue for ABCα subdomains, red for the arm and toe motifs, and magenta for the PtIM30). (b) Equivalently colored stereopair showing a magnified view of one interacting ABC1-ABC2 domain pair in the EttA dimer (generated by deleting 1-286 in protomer A and 278-555 in protomer B), which provides a model for the nucleotide-free conformation of the EttA monomer. Labels indicate the Walker A (WA) motif in the Fl-like core and the LSGGE signature sequence in the ABCα subdomain. The Walker B motif (Φ4DE, with Φ being any hydrophobe and terminating in catalytic base) is located between the WA and LSGGE motifs within each ABC. (c) Stereopair showing models for the nucleotide-free (translucent colors) and ATP-bound (solid colors) conformations of the EttA monomer superimposed via least-squares alignment of ABC2. The nucleotide-free conformation represents one ABC1-ABC2 domain pair from the crystallographically observed EttA dimer (panel b), while the ATP-bound conformation was modeled using rigid-body rotations to align the crystallographically observed nucleotide-free conformations of ABC1 and ABC2 to the two protomers in the ATP-sandwich dimer of the E171Q mutant of MJ0796; see “Structural Superposition” in Online Methods for details. (d) Schematics of the EttA dimer (top), nucleotide-free monomer (middle), and modeled ATP-bound monomer (bottom) colored as above.