FIGURE 2.
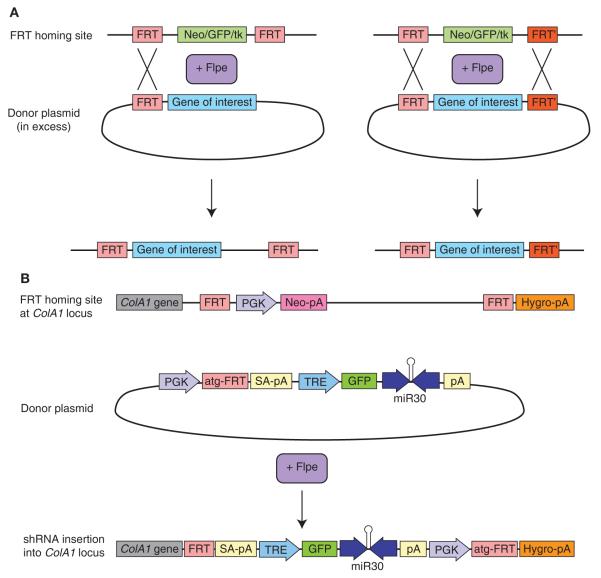
Single-copy shRNA introduction via recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE). (A) RMCE involves the exchange of DNA sequences flanked by recombinase recognition sites between donor and recipient DNA sources. Donor vectors may contain one FRT site for insertion of the complete plasmid or two heterotypic FRT sites for insertion of the intervening plasmid segment. Cotransfection of FLP recombinase with an excess of donor plasmid harboring the gene of interest flanked by FRT recognition sites results in gene insertion into a homing cassette containing the same FRT sites. (B) System for inserting a single-copy shRNA into a defined genomic locus (based on RMCE system of Beard et al. 2006). ES cells are targeted with a FRT homing cassette at the ColA1 locus. The cassette contains an FRT-flanked neomycin resistance gene as well as a hygromycin resistance gene that is missing the ATG start codon. The ES cell line also carries an M2-rtTA, introduced into the Rosa26 locus by homologous recombination to enable doxycyclineinducible gene expression. The donor “FLP-in” vector contains a PGK promoter and an ATG codon followed immediately by an FRT site. The vector also includes a minimal tetracycline-responsive CMV (TRE) promoter, followed by the gene of interest or shRNA. A splice acceptor and polyadenylation site upstream of the TRE promoter minimizes readthrough from the ColA1 promoter. Coelectroporation of the FLP-in vector and a CAGGS promoter–driven FLP result in incorporation of the entire vector between the FRT sites in the ColA1 homing cassette. The PGK promoter and start codon are positioned adjacent to and in frame with the hygromycin resistance gene. Correctly integrated clones can therefore be selected with hygromycin treatment.