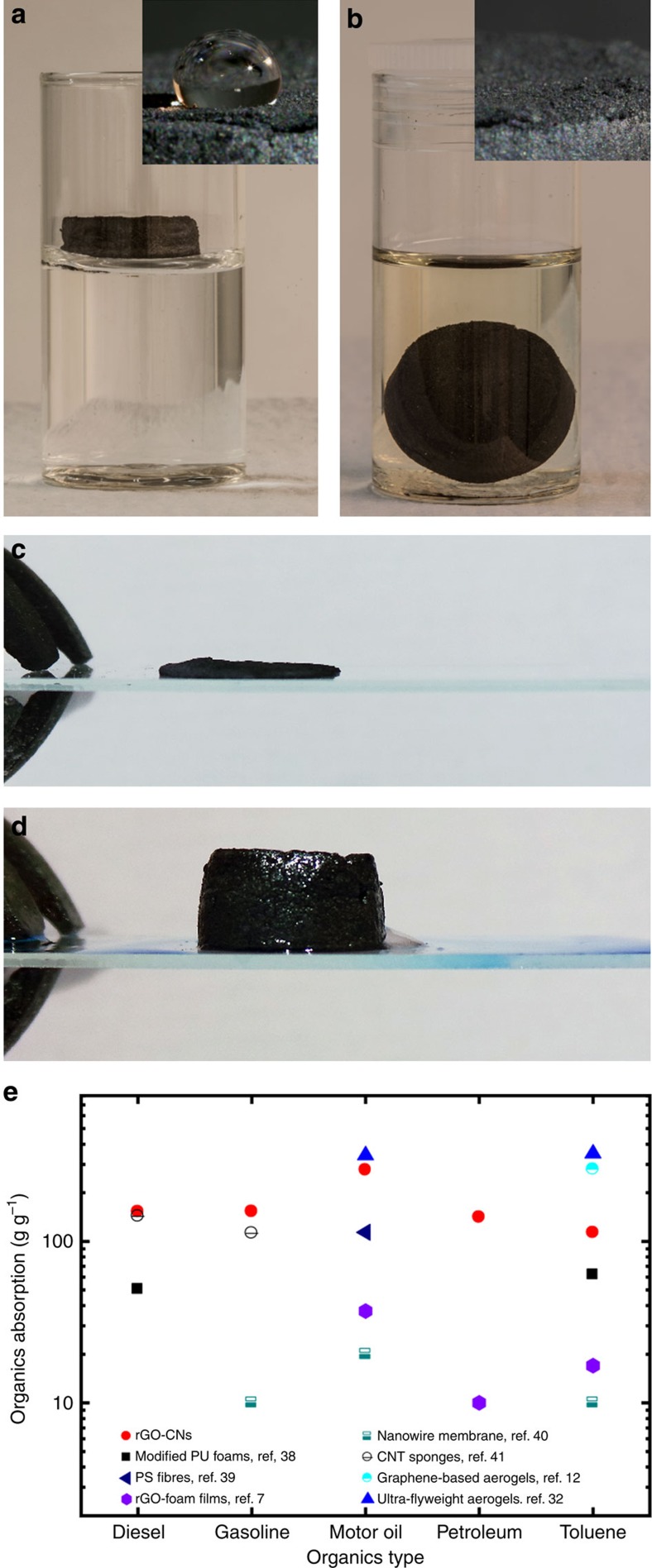
Figure 8. rGO-CNs capability for organics absorption, wetting behaviour and recycling approach.
(a) The rGO-CN floats when in contact with water due to its superhydrophobic properties. Water droplet forms a contact angle of 114° with the rGO-CN surface (insert). (b) rGO-CN rapidly absorbs gasoline filling the highly porous structure with the solvent resulting on its immersion in the gasoline vial. In the insert, gasoline trace left after infiltration in the rGO-CN. (c,d) Recycling approach for rGO-CNs absorbers. After each absorption cycle, the oil phase can be ‘squeezed out’ of the rGO cellular absorber by compressing it (c) and the compressed structure can be directly re-utilized by immersing it in the oil phase again. The absorber immediately expands to its original shape by the absorption of the oil phase within its structure (d) (details in Supplementary Movie). (e) Organics absorption (g g−1) of rGO-CNs in comparison with several absorbers reported in literature for different organic solvents and oils. The rGO cellular absorbers tested (4–4.5 mg cm−3) were produced with 1.2 wt% additives in GO-sus (0.65 wt% GO) and thermally treated at 1,000 °C in Ar/H2 atmosphere.