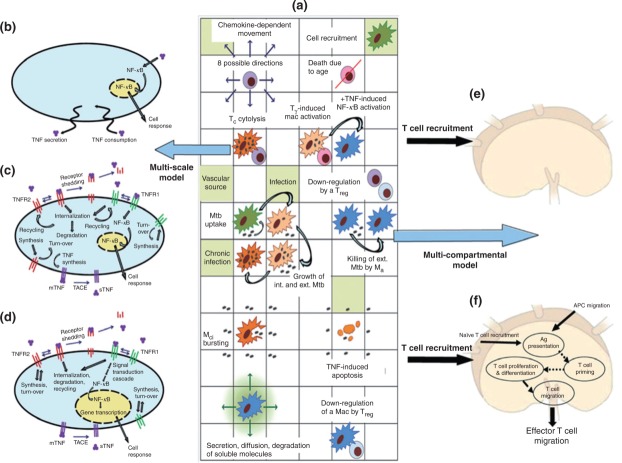
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the multi-scale multi-compartment model of the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. (a) An overview of selected agent-based model (ABM) rules of interaction between host cells, bacteria and lung environment as implemented in GRANSIM69,70 which focuses on cellular and tissue scale dynamics. (b–d) Molecular-scale tumor necrosis factor (TNF) sub-model that can be embedded at three levels of resolution [coarse (b), intermediate (c), fine (d)] in GRANSIM. The molecular-scale model for TNF (c) is described in Ref 11 and when implemented in the granuloma model is termed GRANSIMTNF (Example 1). The molecular-scale model for NF-κB (d) is described in Ref 82 and when implemented in the granuloma model is termed GRANSIMTNF-NFKB (Example 2). (e and f) The lymph node (LN) dynamics are described as in Ref 94 at two levels of resolution [coarse (e), fine (f)] (Example 3). Abbreviations: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), macrophage (mac), antigen (Ag), chronically infected macrophage (Mci), activated macrophage (Ma), pro-inflammatory IFN-γ producing T cell (Tγ) cytotoxic T cell (Tc), regulatory T cell (Treg), TNF-α converting enzyme (TACE), TNF receptor types 1 and 2 (TNFR1, TNFR2), membrane and soluble forms of TNF (mTNF, sTNF).