Figure 7.
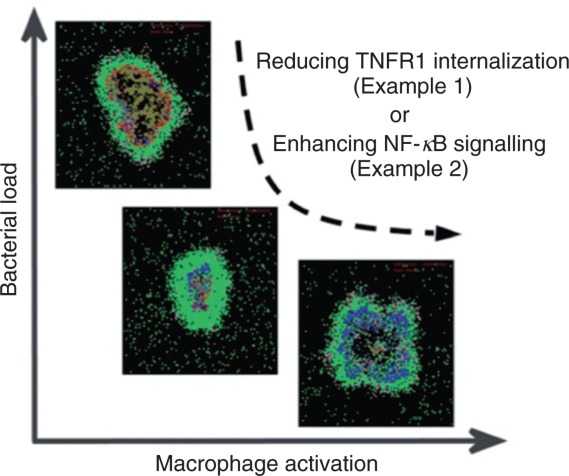
Congruent behaviors achieved from two model resolutions. The predicted roles of TNF R1 internalization and NF-κB signaling in determining granuloma outcomes are shown. Simulations with GRANSIMTNF (Example 1) show that reducing TNFR1 internalization enhances bacterial killing and increases the probability of bacterial clearance. However, the increased TNF concentrations that result give rise to excessive macrophage activation and increased tissue inflammation. Simulations with GRANSIMTNF-NFKB (Example 2) show that containment of bacteria is achieved when a balance exists between the NF-κB-mediated bacterial killing activities and the NF-κB-mediated inflammation. These levels of model resolution are well-suited to exploring potential pharmacological interventions of the signaling pathway. Snapshots of granulomas follow the same color mapping for cells as in Figure 5. The range of behaviors simulated with the two resolutions shows model congruency (see Figure 3).
