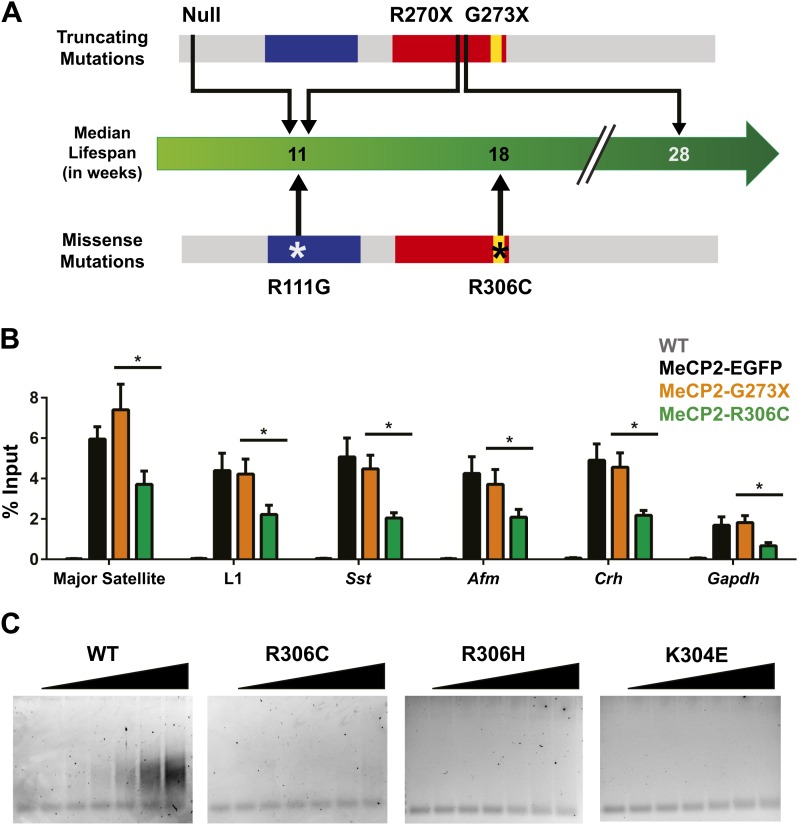
Figure 7. R306C decreases the affinity of the C-terminus of MeCP2 to DNA and reduces its DNA occupancy.
(A) An overview of the lifespans of RTT mouse models emphasizes the fact that the R306C missense mutation is more detrimental than an earlier truncation at G273X. Full-length MeCP2 (gray) with the MBD (blue), TRD (red), and basic cluster (yellow) is depicted. The top shows truncating mutations, while the bottom shows the missense mutations we generated. The median lifespans of mice carrying the mutations are shown in weeks. (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) using an anti-GFP antibody followed by quantitative PCR (qPCR) to determine enrichment of the following amplicons: Major Satellite repetitive sequences, L1 retrotransposons (L1), somatostatin (Sst), afamin (Afm), corticotropin releasing hormone (Crh), and Gapdh shows that MeCP2-R306C has decreased binding to sequences known to be bound by MeCP2 in vivo. Comparing MeCP2-R306C (green, n = 7) to MeCP2-G273X (orange, n = 7) shows that the differences observed are due to an additional effect of the C-terminus that is absent in the full-length MeCP2-EGFP (black, n = 4). WT mice with no GFP (gray, n = 3) were used as a negative control. (C) An electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) using increasing amounts of N-terminally GST-tagged C-terminal human MeCP2 recombinant protein (amino acids 274–340, from left to right: WT, R306C, R306H, K304E) shows that the WT C-terminal fragment of MeCP2 can bind DNA and that RTT-causing mutations altering the charge of basic residues in the fragment abolish this binding. Data were analyzed by an ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Results were plotted as the mean ± SEM. *p<0.05.