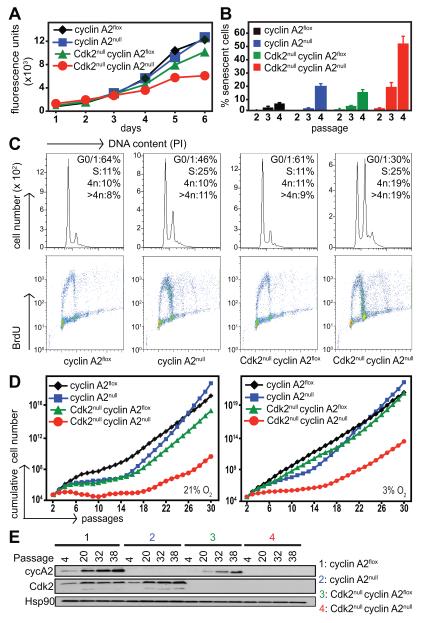
Fig. 4. Concomitant loss of Cdk2 and cyclin A2 results in impaired proliferation and premature senescence.
Primary cyclin A2flox and Cdk2nullcyclin A2flox MEFs were treated with 4-OHT to induce cyclin A2 knockout and their proliferative potential was determined by alamarBlue proliferation assays (A). Cdk2nullcyclin A2null MEFs display impaired proliferation rates when compared to other genotypes. Loss of cyclin A2 and Cdk2 resulted in an increased number of prematurely senescent cells in early passages, as detected by β-galactosidase staining (B). Analysis of cell cycle profile by BrdU labeling and propidium iodide (PI) staining revealed increased population of cells in S phase, and cells with 4n and >4n DNA content in Cdk2nullcyclin A2null cells (C). Data is representative of three independent MEF lines. Cyclin A2flox and Cdk2nullcyclin A2flox MEFs were treated with 4-OHT to induce cyclin A2 knockout and were cultured over several passages using a 3T3 assay at 21% (left panel) and 3% (right panel) oxygen to determine long-term propagative potential (D). Of 7 clones tested, only one Cdk2nullcyclin A2null clone survived the 3T3 assay at 21% oxygen. MEFs were collected at various passages during the course of the 3T3 assay at 21% oxygen conditions and the absence of cyclin A2 protein in cyclin A2null and DKO MEFs was confirmed by Western blotting of protein extracts (E).