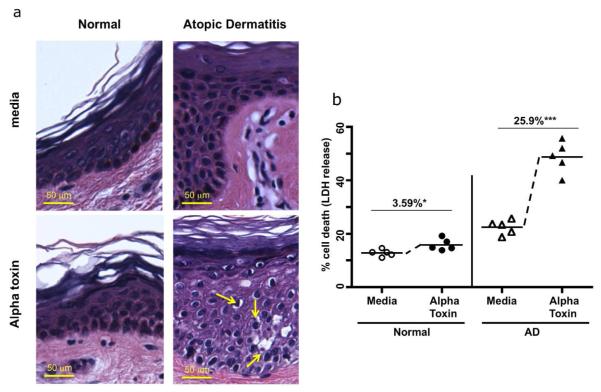
Fig 1. Increased staphylococcal alpha toxin induced cell death in atopic dermatitis skin.
(A) Panels show skin biopsies from normal and AD patients treated with media or alpha toxin, and stained by H&E. Increased cell damage (indicated by pyknotic cells with reduced cytoplasmic staining) is observed in AD biopsies compared to controls. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Quantification of cell death induced by alpha toxin treatment (12.5ng/ml 24 h) in skin biopsies from normal (n = 5) and AD patients (n = 5) was determined by LDH release. The LDH release induced by alpha toxin was calculated by subtracting out the baseline induced by media. Mean percent alpha toxin induced cell death ± SEM in control skin is 3.59% ± 1.20 (* p < .05 as compared to media cultured biopsies): mean alpha toxin induced cell death in AD is 25.9% ± 3.31, and was significantly different from control skin (*** p < 0.001 as compared to media cultured biopsies).