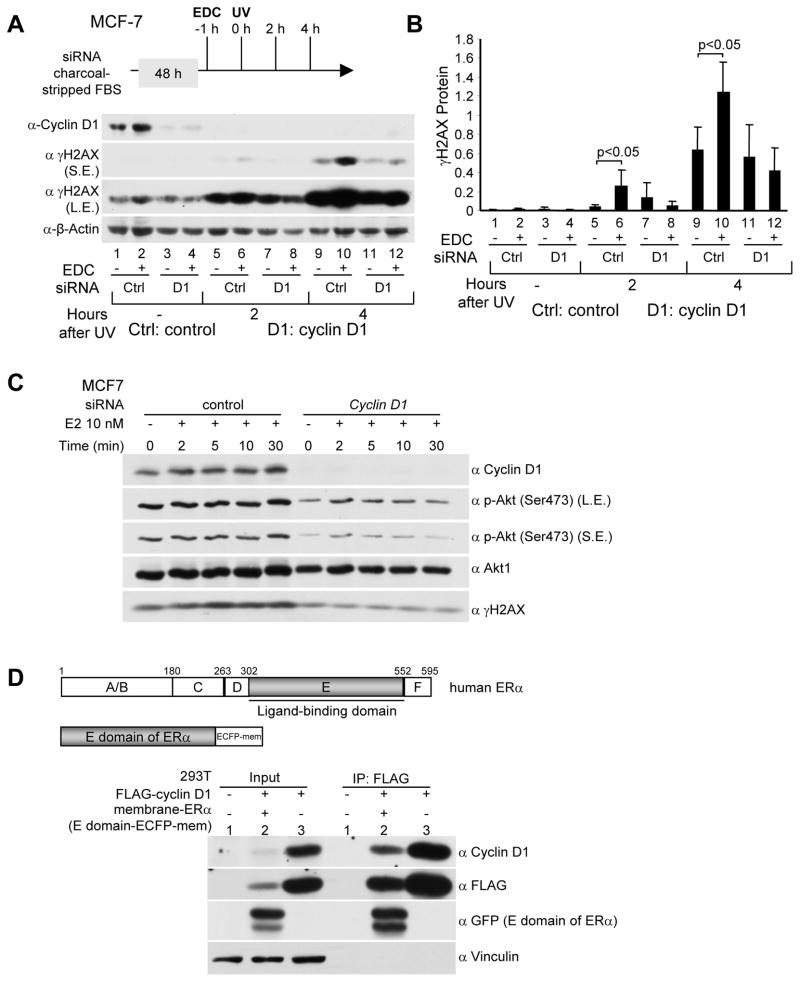
Figure 3. Endogenous cyclin D1 mediates the cytoplasmic membrane mediated E2-dependent DNA damage response.
(A) Western blot analysis of MCF-7 cells treated with cyclin D1 siRNA and EDC (estrogen-dendrimer conjugate) at a dose equivalent to 10−8M E2. Western blot analysis was conducted using antibodies directed to γH2AX, cyclin D1 or β-actin as a protein loading control (SE, short exposure, LE, long exposure). (B) Quantitation of relative γH2AX protein abundance shown as mean ±SEM for N>3 separate experiments. (C) Endogenous cyclin D1 enhances E2-induced Akt phophorylation (Ser473) in MCF-7 cells exposed to UV. MCF-7 cells were transfected with cyclin D1 siRNAs or control siRNA. 48 hrs later cells were treated with 10 nM E2 for time points as indicated. Then cells were exposed to UV (100 J/m2). Specific antibodies to phospho-Serine 473 Akt1/2/3, total Akt1, and γH2AX were used in Western blot analysis. (D) Membrane E domain of ERa binds to cyclin D1 in 293T cells. 293T cells were co-transfected with FLAG-cyclin D1 (in CMV10 vector) and the E domain of ERα (in ECFP-Mem vector targeting the E domain to the plasma membrane). 48 hrs later immunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis were conducted to detect membrane-ERα and FLAG-cyclin D1 interaction.