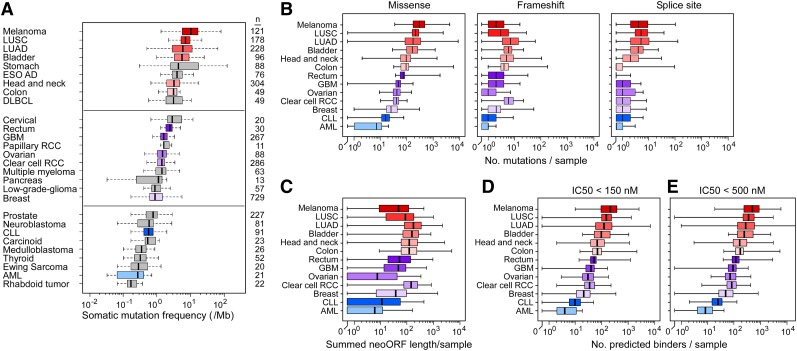
Figure 7.
Estimation of tumor neoantigen load across cancers. (A) Box plots comparing overall somatic mutation rates detected across cancers by massively parallel sequencing. AML, acute myeloid leukemia; DLBCL, diffused large B-cell lymphoma; ESO AD, esophageal adenocarcinoma; GBM, glioblastoma; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; clear cell RCC, clear cell renal carcinoma; papillary RCC, papillary renal cell carcinoma. The distributions (shown by box plot) of (B) the number of missense, frameshift, and splice-site mutations per case across 13 cancers, (C) the summed neoORF length generated per sample and of the predicted neopeptides with (D) IC50 <150 and (E) <500 nM generated from missense and frameshift mutations. For all panels, the left and right ends of the boxes represent the 25th and 75th percentile values, respectively, and the segment in the middle is the median. The left and right extremes of the bars extend to the minimum and maximum values.