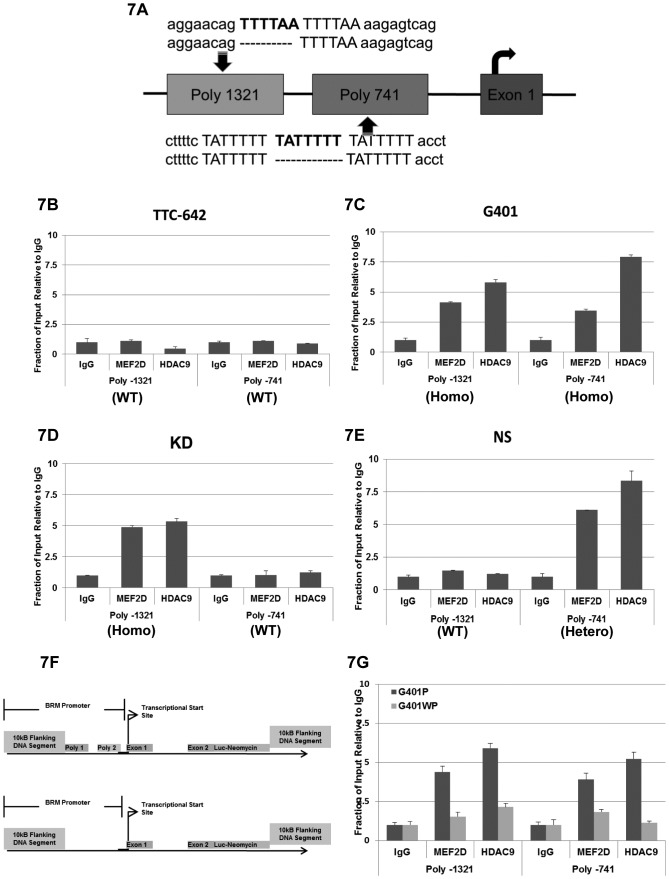
Figure 7. A illustrates the two BRM insertion polymorphisms (in bold), -1321 and -741, which are 1321 bp and 741 bp, respectively, upstream of the transcription start site.
The 1321 polymorphic site is a duplicate repeat of the “TTTTAA” sequence, whereas the -741 polymorphic site is a triplicate repeat of the “TATTTTT” sequence. The position of the first exon is shown as well as curved arrow, which designated the transcription start site. The wild type or nonpolymorphic sites are represented by the absence of the additional sequence (polymorphic site) by a broken line located underneath of the polymorphic sequence. B Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was conducted in the BRM-positive cell line, TTC642 (wild type for Poly-1321/Poly-741) to determine whether HDAC9 and/or MEF2D can bind to the BRM promoter. No significant bindings of either MEF2D or HDAC9 were observed in TTC642 (p>0.05), compared to the IgG control. C ChIP was conducted in the BRM-negative Rhabdoid cell line, G401 (homo/homo for Poly-1321/Poly-741), to assess HDAC9 and/or MEF2D binding to the BRM promoter. Binding of both HDAC9 and MEF2D to the G401 promoter was observed at or near both the Poly 1321 and Poly 741 sites (p<0.05, compared to IgG control). D ChIP was conducted in the BRM-negative Rhabdoid cell line, KD (homo/wild type for Poly-1321/Poly-741), for HDAC9 and/or MEF2D binding to the BRM promoter. Binding of both HDAC9 and MEF2D to the BRM promoter at or near the Poly 1321 site was observed (p<0.05, compared to the IgG control), but no binding to the BRM promoter at or near the Poly 741 (wild type) site was observed (p>0.05, compared to the IgG control). E ChIP was conducted in the BRM-negative Rhabdoid cell line, KPMRT-NS (wild type/hetero for Poly-1321/Poly-741), for the binding of HDAC9 and/or MEF2D to the BRM promoter. Binding of both HDAC9 and MEF2D to the BRM promoter at or near the Poly-741 (hetero) site (p<0.05, compared to IgG control) was observed, but no binding of either HDAC9 or MEF2D to the BRM promoter at or near the Poly 1321 (wild type) site (p>0.05, compared to IgG control) was observed. F illustrates the BRM promoter reporter construct. This construct consisted of 10kb upstream of the BRM promoter as well as 10kb downstream of the translational start site. The luciferase gene linked was to the IRES-neomycin gene at the beginning of the translational site, with or without the two BRM polymorphic sites present in the BRM promoter. G shows the results of the ChIP experiment using the BRM luciferase reporter construct, where the BRM promoter contains either the presence (G401P) or absence (G401WP) of the two BRM polymorphic sites. When the BRM polymorphic sites were present (G401P), HDAC9 and MEF2D were found to bind to the BRM promoter at or near each BRM polymorphic site, respectively, whereas in the absence of these two BRM polymorphic sites (G401WP), HDAC9 and MEF2D demonstrated a lack of specific binding; that is, the binding was comparable to nonspecific IgG, which was used as a control.