Table 3.
Influence of Reaction Conditions[a]
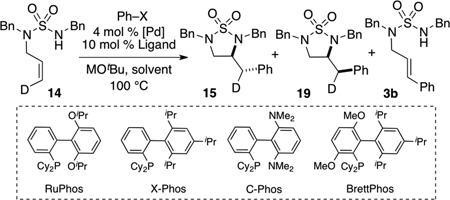 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | X | Ligand | M | Solvent | 15:19[b] | (15+19):3b[c] |
| 1 | OTf | RuPhos | Li | PhCF3 | >20:1 | 99:1 |
| 2 | OTf | RuPhos | Na | Toluene | 7:1 | 94:6[d] |
| 3 | OTf | X-Phos | Na | Toluene | 1:7 | 72:28[d] |
| 4 | OTf | X-Phos | Li | Dioxane | 1:10 | 60:40 |
| 5 | OTf | X-Phos | Li | PhCF3 | 10:1 | 93:7 |
| 6 | Br | X-Phos | Na | Toluene | 1:4 | 70:30[d] |
| 7 | Br | RuPhos | Na | Toluene | 1:1 | 60:40[d] |
| 8 | Br | RuPhos | Na | Toluene | 1:1 | 60:40 |
| 9 | Br | RuPhos | Na | PhCF3 | 10:1 | 93:7 |
| 10 | Br | X-Phos | Na | PhCF3 | 1:1 | 60:40 |
| 11 | Br | BrettPhos | Na | PhCF3 | 10:1 | 98:2 |
| 12 | Br | C-Phos | Na | PhCF3 | >20:1 | 99:1 |
Reaction Conditions: 1.0 equiv 14, 1.2 equiv Ph–X, 1.4 equiv MOtBu, 4 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 10 mol % Ligand, Solvent (0.0625 M), 100 °C.
NMR ratio of 15:19.
NMR Ratio of (15+19):3b. In general, no significant amounts of other side products were generated in these reactions, and NMR yields are estimated to be >90% for the combined total of 15+19+3b.
Pd2(dba)3 (2 mol % complex, 4 mol % Pd) was used in place of Pd(OAc)2.
