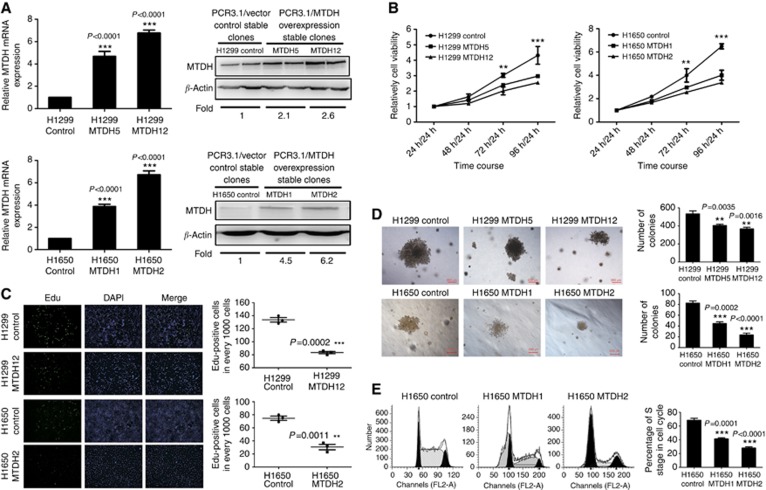
Figure 2.
MTDH expression inhibits NSCLC cell proliferation in vitro. (A) Q-PCR and western blotting analyses for expression of MTDH in H1299 and H1650 control clones, selected stably transfected high MTDH-expressing clones (H1299 MTDH12 and H1650 MTDH2) and lowMTDH-expressing clones (H1299 MTDH5 and H1650 MTDH1). GAPDH and β-actin were, respectively, used as control for mRNA and protein. Fold of MTDH expression was normalised to the expression of control cells. ***P<0.0001 compared with vector control cells. (B) MTT assay of H1299/H1650 control and MTDH-overexpressing H1299/H1650 cells. Cell absorbance at 24 h was used as reference. Cell proliferation in MTDH-overexpressing cells was significantly decreased at 72 h/24 h and 96 h/24 h. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with vector control cells. (C) EdU cell proliferation assay of H1299/H1650 control and MTDH-overexpressing H1299/H1650 cells. ***P=0.0002 compared with vector control cells. The numbers of EdU-binding cells in MTDH-overexpressing H1299/H1650 cells were significantly reduced. **P=0.0011 compared with vector control cells. (D) Anchorage-independent growth ability. Colony size was smaller in MTDH-overexpressing H1299/H1650 cells, and the number of colonies in MTDH-overexpressing H1299/H1650 cells was significantly reduced. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with vector control cells. (E) Cell cycle analysis of H1650 vector control and MTDH-overexpressing cells. The percentage of S phase in cell cycle was significantly decreased in MTDH-overexpressing cells. Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.05 compared with vector control cells.