Figure 3. EB1 knockdown in colon cancer cell lines induced changes in proliferation and apoptosis.
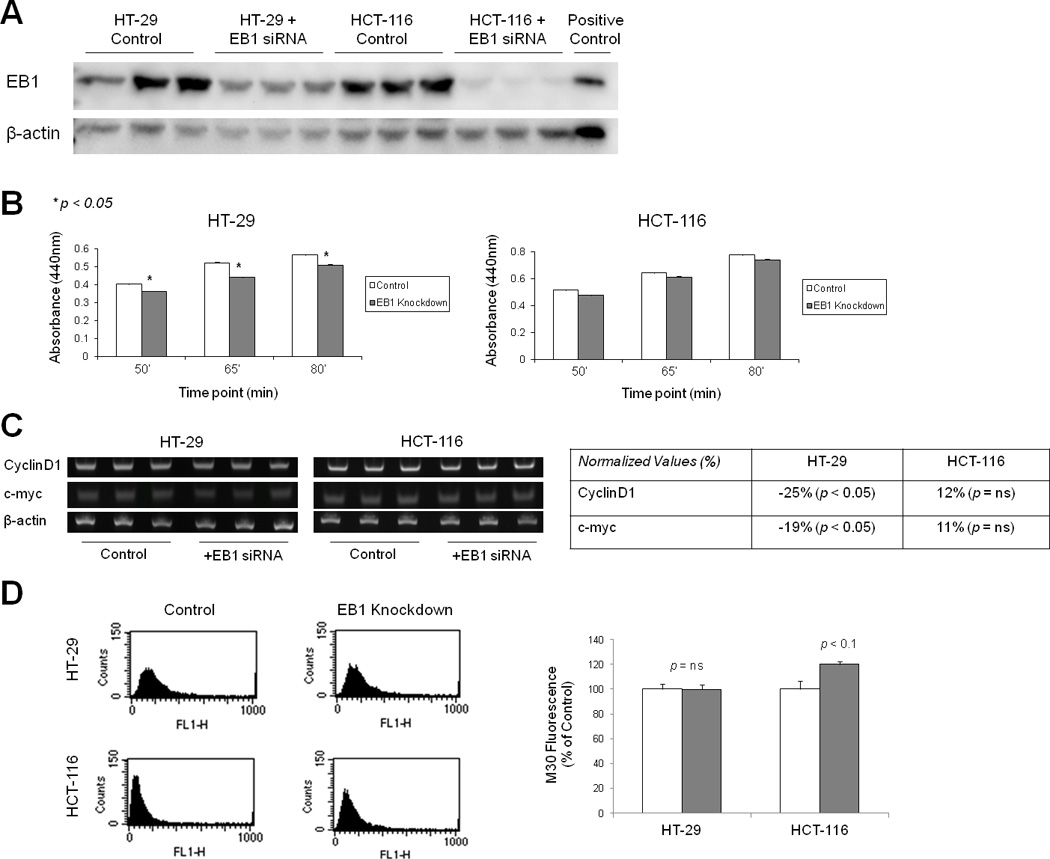
A) Western Blotting indicates 60–80% loss of EB1 in HT-29 and HCT-116 cell lines following siRNA-mediated knockdown. B) WST-1 assay showed that EB1 knockdown decreased HT-29 cell proliferation (p <0.05) but did not significantly affect HCT-116 cells. C) Knockdown of EB1 decreased cyclinD1 and c-myc expression in APCmut/mut HT-29 cells, but did not affect expression of these Wnt pathway members in APCwt/wt HCT-116 cells, using PCR. Expression was normalized to β-actin, *p <0.05. D) Control and EB1 knockdown cells were then subjected to flow cytometric analysis to measure M30 (apoptosis marker) levels. EB1 knockdown induced apoptosis in APCwt/wt HCT-116 cells (120% of control; p =0.06), it did not affect apoptosis in APCmut/mut HT-29 cells. Error bars represent standard error.
