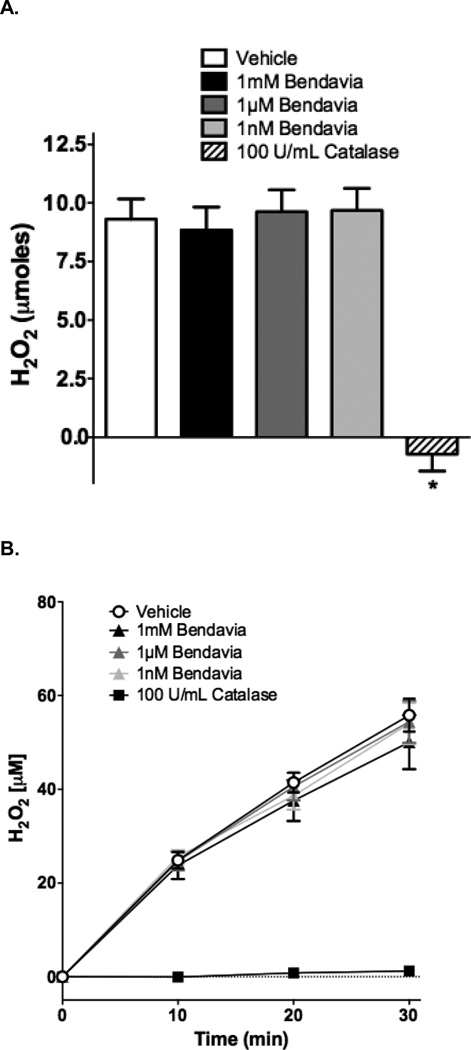
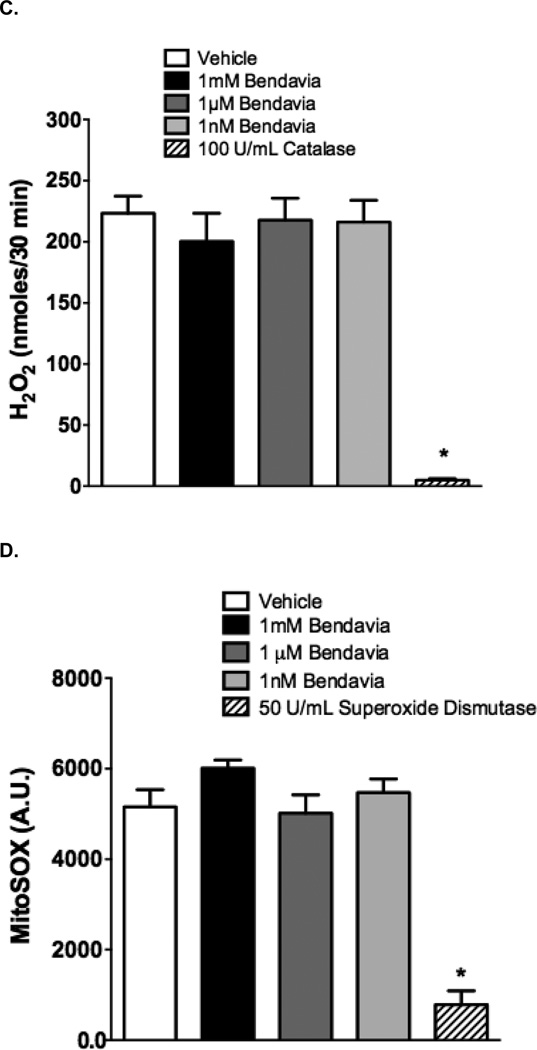
Figure 7.
Lack of ROS-scavenging capacity of Bendavia in in vitro, cell-free systems. The ability of Bendavia to scavenge ROS (specifically H2O2) was tested with either a static H2O2 incubation (A), or a dynamic glucose-glucose oxidase reaction, which generates H2O2 as a reaction product (B). The net amount of H2O2 produced under each condition in B was calculated after 30 minutes of the glucose-glucose oxidase protocol, and are presented in (C). H2O2 levels were assessed by Amplex Red fluorescence. Bendavia did not influence H2O2 levels across a wide range of concentrations tested, in clear contrast to the positive control catalase. D. Additionally, the superoxide (O2•−) scavenging capacity of Bendaiva was tested using a xanthine-xanthine oxidase reaction. Bendavia also showed no observable scavenging capacity for O2•−, in contrast to the positive control superoxide dismutase (SOD). *, P<0.05 (ANOVA).