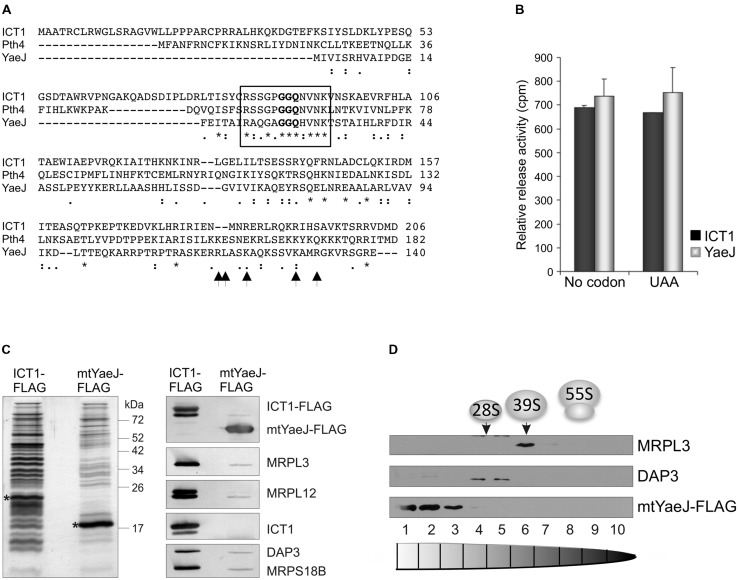
FIGURE 1.
ICT1 as a mitochondrial translation rescue factor and its possible orthologs. (A) Alignment of human ICT1 (14197) with the Pth4 ortholog from S. pombe (Q9HDZ3) and YaeJ ortholog from E. coli (E2QFB9). Identity is indicated by (*), high levels of similarity by (:) and lower levels by (⋅). The conserved GGQ region is boxed and the YaeJ residues that are required for PTH activity and are highly conserved between bacterial species are indicated by arrows. (B) Release activity of recombinant YaeJ and ICT1. PTH activity was tested on 70S ribosomes primed with either no RNA or UAA triplet in the A-site. (C) Mitochondrial targetted YaeJ-FLAG shows interaction with human mitochondrial ribosomal proteins. FLAG tag mediated immunoprecipitations of ICT1 and mitochondrially targeted YaeJ were performed on lysates of HEK293 cell lines induced for 3 days. The elution fractions (10%) were separated by SDS PAGE and analyzed by silver staining (left panel, FLAG protein indicated by *) or western blot (right panel). Antibodies against MRPL3, MRPL12, ICT1, DAP3, and MRPS18B were used to determine the relative levels of coimmunoprecipitated ribosomal proteins. The presence of FLAG tagged protein in each elution was confirmed by anti-FLAG antibodies. (D) Mitochondrially-targeted YaeJ-FLAG does not co-migrate with the 39S LSU. Lysate (700 μg) of mtYaeJ-FLAG expressing cells was separated on an isokinetic sucrose gradient. Fractions were analyzed by western blot using antibodies against the 39S LSU (MRPL3) and the 28S SSU (DAP3). The distribution of mtYaeJ-FLAG was determined by applying FLAG antibodies. Methods for panels (B–D) were essentially as described in Richter et al. (2010), except a YaeJ-FLAG construct was used to generate a HEK293T overexpression line instead of the ICT1 FLAG.