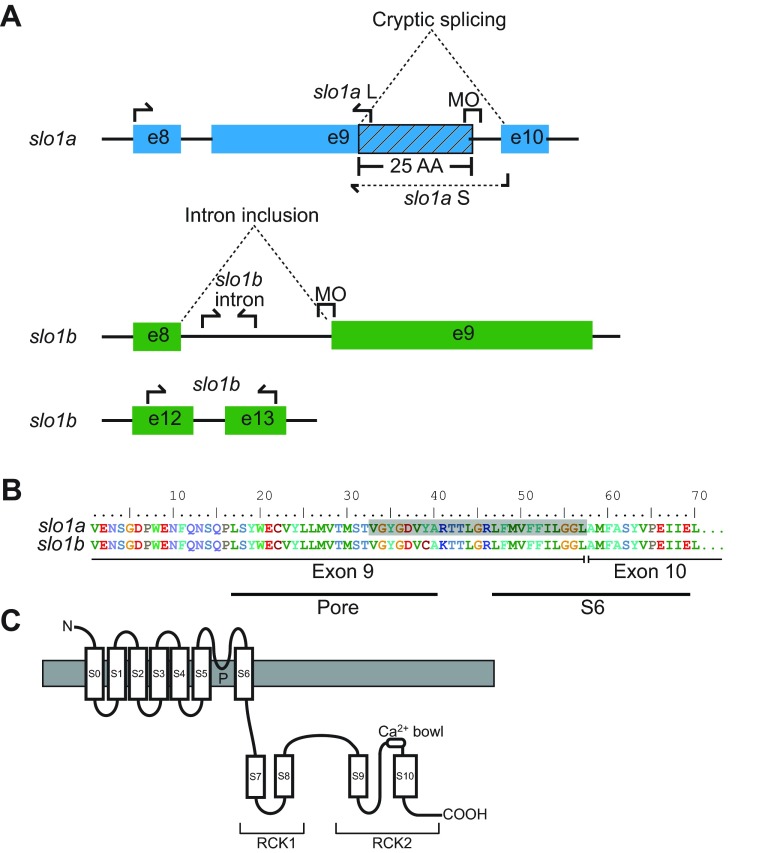
Fig. 1.
slo1a and slo1b splice-blocking morpholino and qPCR design. (A) A splice-blocking morpholino (MO) was designed targeting exon 9 (e9) of slo1a. This MO causes activation of a cryptic splice site resulting in a truncation of the protein encoded by e9 by 25 amino acids (AA, hatched box). Primers (arrows) were designed to measure transcript abundance of both intact (L) and truncated (S) slo1a as well as slo1b. A splice-blocking MO was designed targeting exon 9 (e9) of slo1b. This MO caused inclusion of the intron between exons 8 and 9 resulting in the introduction of stop codons between e8 and e9, causing a loss of pore, S6 and intracellular C-terminal tail domains. (B) The 25 amino acid region of e9 removed by the slo1a MO corresponds to the final third (8 of 24 amino acids) of the BK channel pore and approximately the first half (11 of 23 amino acids) of the S6 transmembrane domain. Amino acid numbering is just for scale and does not reflect amino acid number within the entire BK channel protein. (C) Schematic diagram of the BK channel α-subunit encoded by each slo1 gene.