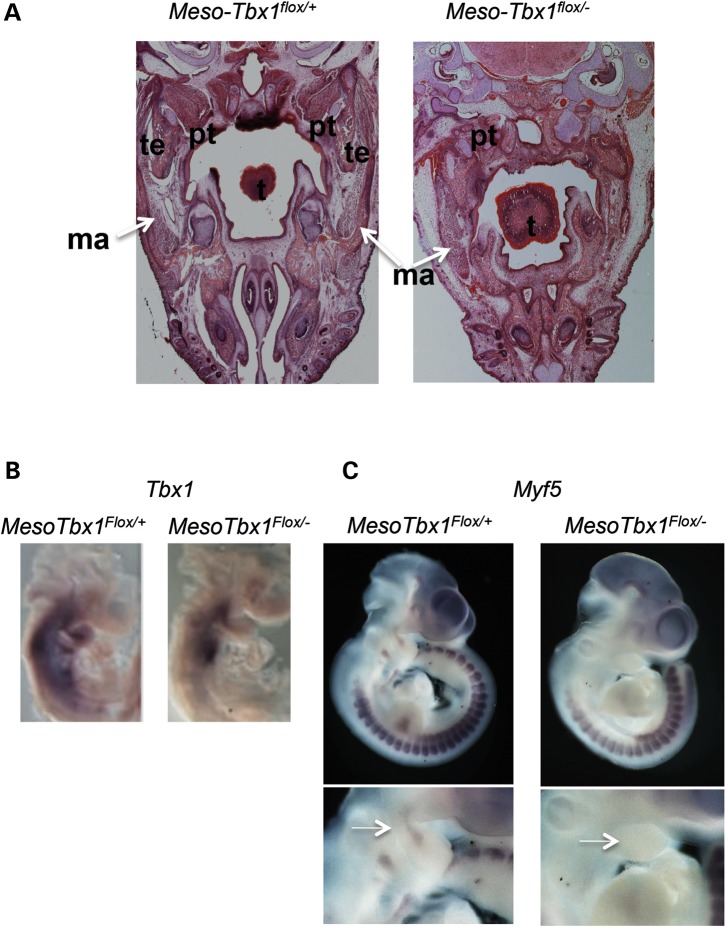
Figure 9.
Mesodermal Tbx1 is required to form the muscles of mastication. (A) Transverse histological sections of Mesp1Cre/+; T-Cre; Tbx1flox/+ and Mesp1Cre/+; T-Cre; Tbx1flox/− (MesoTbx1flox/+ or MesoTbx1flox/−) embryos at E17.5 stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Adipocytes have largely replaced muscles of mastication (right). The masseter muscle is present unilaterally, but hypoplastic, and a pterygoid muscle is present unilaterally (additional images are in the Supplementary Material, Fig. S3), but again, is severely hypoplastic. ma = masseter. (B) Lateral views of whole-mount in situ hybridization of antisense probe for Tbx1 in MesoTbx1flox/+ and MesoTbx1flox/− littermates at E9.5. Mesodermal expression of Tbx1 in heterozygous embryos is greatly reduced, but still present in conditional mutants. (C) Lateral views of whole-mount in situ hybridization of antisense probe for Myf5 in MesoTbx1flox/+ and MesoTbx1flox/− littermates at E10.5. Enlarged pharyngeal region from in situ hybridization images are shown below whole embryo views. Arrow points to the Myf5 core mesoderm expression domain. Expression was diminished in conditional null mutant embryos.