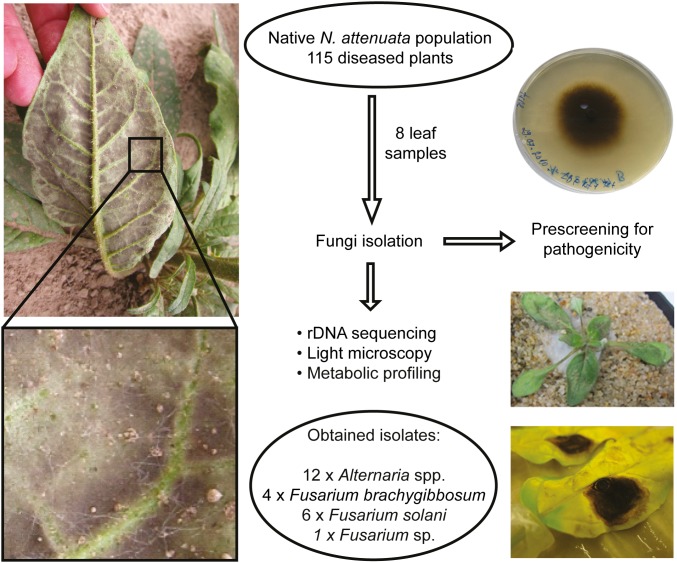
Figure 2. Work flow for the isolation of the native fungal pathogen isolates used in this study.
In a native N. attenuata population plants suffered from disease symptoms (chlorosis, curly leaves and dark mycelium-like structures on the abaxial side, illustrated on the left). Leaf samples were taken from diseased plants for fungi isolation. Pathogenicity of the isolates was evaluated using different infection methods. Fungi, which were able to cause severe disease symptoms on plants were re-isolated from infected plant material and further characterized by rDNA sequencing, microscopy and their polar metabolite profiles, resulting in 12 Alternaria spp., 4 Fusarium brachygibbosum, 6 F. solani and one Fusarium sp. isolates.