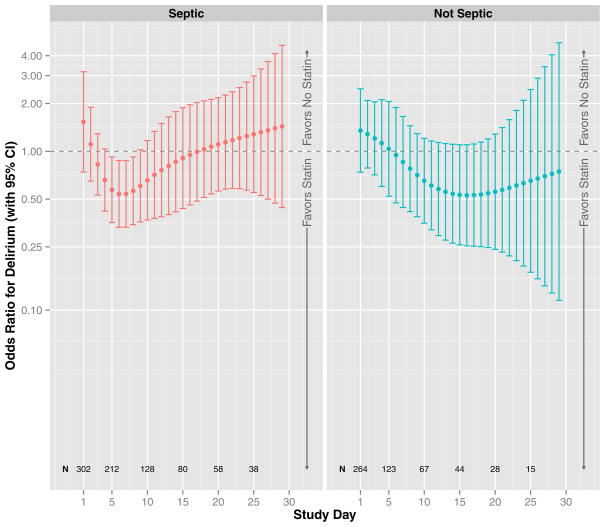
Figure 3. Prehospital Statin Use and Delirium.
The odds ratio for delirium that was associated with prehospital statin use, after adjusting for covariates, is indicated by the dark circles (with corresponding 95% confidence intervals indicated by vertical lines); results are shown according to the study day (indicated by position along the x-axis) and the presence or absence of severe sepsis (left and right panels, respectively); N displays the number of patients in the cohort on specific study days, which changes over time due to discharge, death, and changing sepsis status. After adjusting for age, baseline cognitive function, Framingham Stroke Risk Profile, propensity score of prehospital statin use, severity of illness, sepsis, mechanical ventilation, sedative and analgesic doses, steroid use, and study day, prehospital statin use was not associated with delirium (p = 0.21).