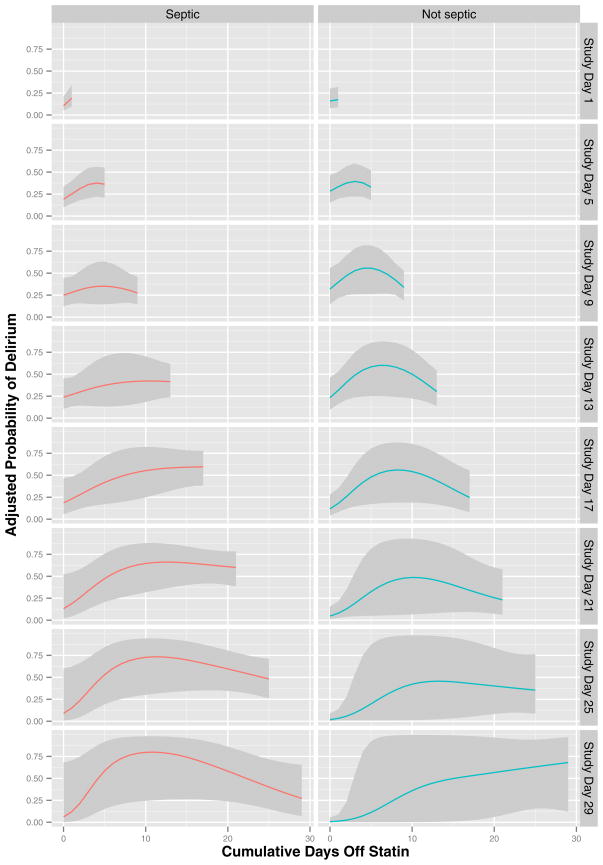
Figure 4. Duration of Statin Discontinuation and Delirium.
The probability of delirium that was associated with the duration of statin discontinuation, after adjusting for covariates, is indicated by the colored lines (with corresponding 95% confidence intervals indicated by gray ribbons); results are shown according to study day (indicated by position along the x-axis) and the presence or absence of sepsis (left and right panels, respectively). After adjusting for age, baseline cognitive function, Framingham Stroke Risk Profile, propensity score for prehospital statin use, severity of illness, sepsis, mechanical ventilation, sedative and analgesic doses, steroid use, and study day, longer durations of statin discontinuation among prehospital statin users were associated with increased delirium (p < 0.001), with the association significantly modified by sepsis and by study day (both interaction p < 0.001).