Figure 2.
Hfq Binds an ARN Motif Adjacent or Overlapping the mRNA Seed Sequence
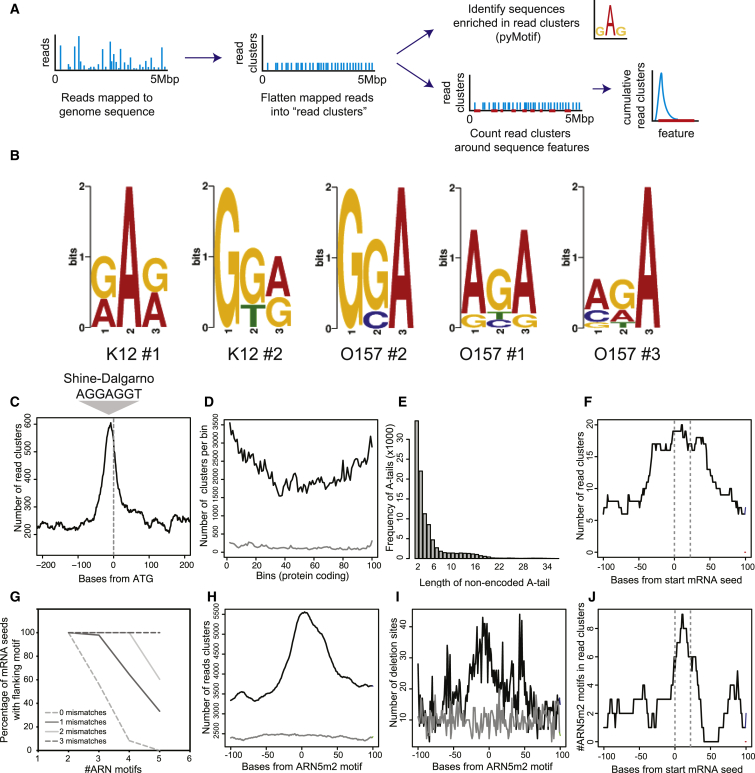
(A) Workflow for analysis of Hfq crosslinked reads. Mapped reads were flattened into read clusters to prevent bias toward highly enriched sites. Read clusters are analyzed for enriched motifs (as in [B]) or their culmulative distrubution around sequence features such as CDS and mRNA seed regions (as in [C]–[J]).
(B) pyMotif from the pyCRAC software package was used to identify trimers that were enriched within RNAs crosslinked to Hfq in five independent experiments. Hfq was crosslinked in either nonpathogenic E. coli K12 str. MG1655 (K12) or enterohemorhaggic E. coli O157:H7 str. Sakai (O157). All five logos fit either a repeated AGG or AGA sequence (indicated below).
(C) Cumulative Hfq-bound read clusters are plotted relative to the start codon (indicated by gray dashed line). The sequence and approximate position of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence is indicated above.
(D) Cumulative Hfq binding within coding sequences. CDS were divided into 100 bins and scored for overlapping read clusters. The cumulative score (genome wide) for each bin is indicated in black and the cumulative score for shuffled CDS coordinates in gray (CDS were assigned random positions within the genome).
(E) Frequency of non-genomically encoded oligo(A)-tail length recovered from Hfq-bound reads.
(F) Cumulative Hfq-bound read clusters within 100 nt of experimentally verified mRNA seed sequences. Grey dashed lines indicate the position and width for the average mRNA seed.
(G) Percent of mRNA seeds with ARN motifs within 100 nt allowing mismatched postions. The x axis represents the number of ARN repeats within a motif, and the y axis represents the percentage of mRNA seeds with that motif within 100 nt. The percentage of mRNA seeds with a flanking ARN motif is plotted for zero to three mismatched postions.
(H) Transcriptome-wide cumulative count of Hfq bound read clusters at ARN5m2 motifs (black) and control shuffled ARN5m2 coordinates (gray).
(I) Transcriptome-wide cumulative count of deletions in Hfq-bound read clusters at ARN5m2 motifs (indicating direct Hfq contact; black) and control shuffled ARN5m2 coordinates (gray).
(J) Position of ARN5m2 motifs within Hfq bound reads at experimentally verified mRNA seed sequences (see also Figure S2 for sequences). Grey dashed lines indicate the position and average width of mRNA seed sequences.