Figure 2.
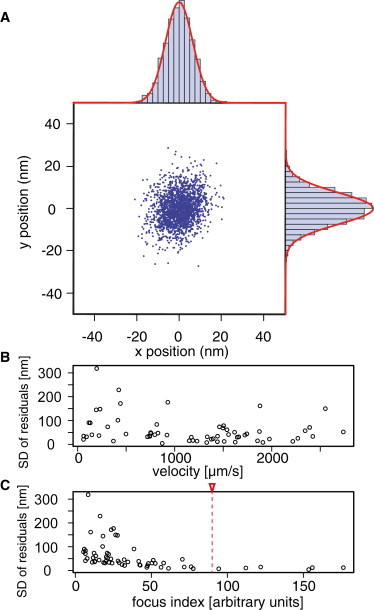
Precision of determining the cell position using the CLONA method. (A) Position of stationary cells for 2000 frames calculated using the CLONA method. The average position of the 2000 frames was used as the origin of coordinate system. (Red solid line) Fitted normal distribution, with σx = 6.5 and σy = 7.4 nm. Pixel size of the original images: 560 nm. (B) The standard deviation of residuals plotted against the velocity of moving cells. The precision varies among cells but does not depend on velocity. (C) The standard deviation of residuals plotted against the focus index. The two variables show a clear inverse relation. For a high focus index, all the targets were located in high-precision region, independent of the velocity. The precision of the CLONA method can be <10 nm, independent of the velocity if cells have a focus index >90 (red dotted line).
