Figure 4.
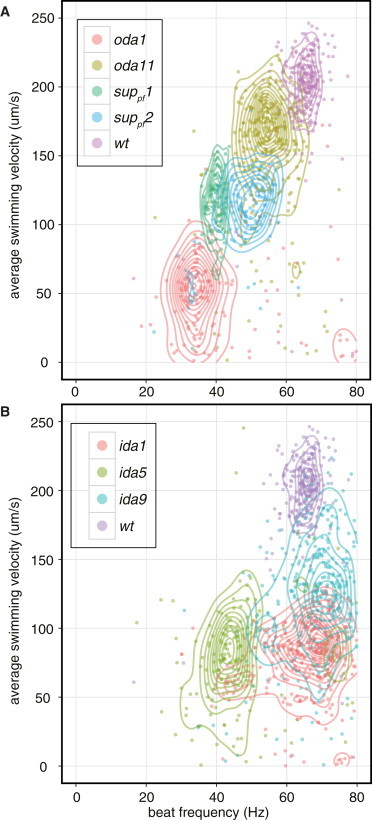
Phenotyping Chlamydomonas mutants based on the CLONA method. Scatter plots of beat frequency f versus average swimming velocity of the beat cycles, generated using the software R (18). Each dot represents one beat cycle, and mutant and wild-type strains are shown with distinct colors. Descriptions of the flagella mutants used here are shown in Table 1. The contour lines were generated to aid with interpreting the distribution of the dots using STAT_DENSITY2D of the GGPLOT2 software package (24), which estimates two-dimensional kernel densities. The difference between the strains are statistically significant (p < 0.001). (A) Scatter plot of beat cycles of four outer dynein arm mutants (oda1, oda11, suppf1, and suppf2) and wild-type. The beat cycles of wild-type and mutants formed a cluster around each characteristic area in the scatter plot. (B) Scatter plot of the beat cycles of three inner dynein arm mutants (ida1, ida5, and ida9) and the beat cycles of wild-type.
