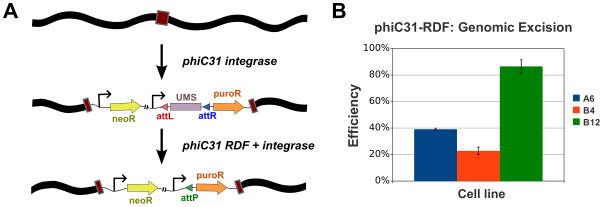
Figure 3. Genomic excision experiment.
(A) Simplified diagram of the selection scheme for LxR excision. Stable lines are made with the pN2B-RTL-puro plasmid by phiC31 pseudo site integration, then isolated through G418 selection. Next, each line was transfected with the pCS-kRI expression vector, which will impart it with resistance to puromycin if the RDF:Int complex can act at the integrated locus, due to excision of the UMS transcription terminator. (B) Normalized excision efficiency. The HeLa pN2B-RTL-puro lines A6, B4 and B12 were transfected in triplicate with pCS-kRI, and puromycin-resistant colonies were obtained in every case. Puromycin-resistant colonies were never obtained from control-vector transformations. Colony counts were normalized to the transfection efficiency of pEGFP-C1 for each line. Representative data from one of two independent trials is shown here. The mean efficiency of each line was plotted here with error bars that indicate the standard error of the mean.