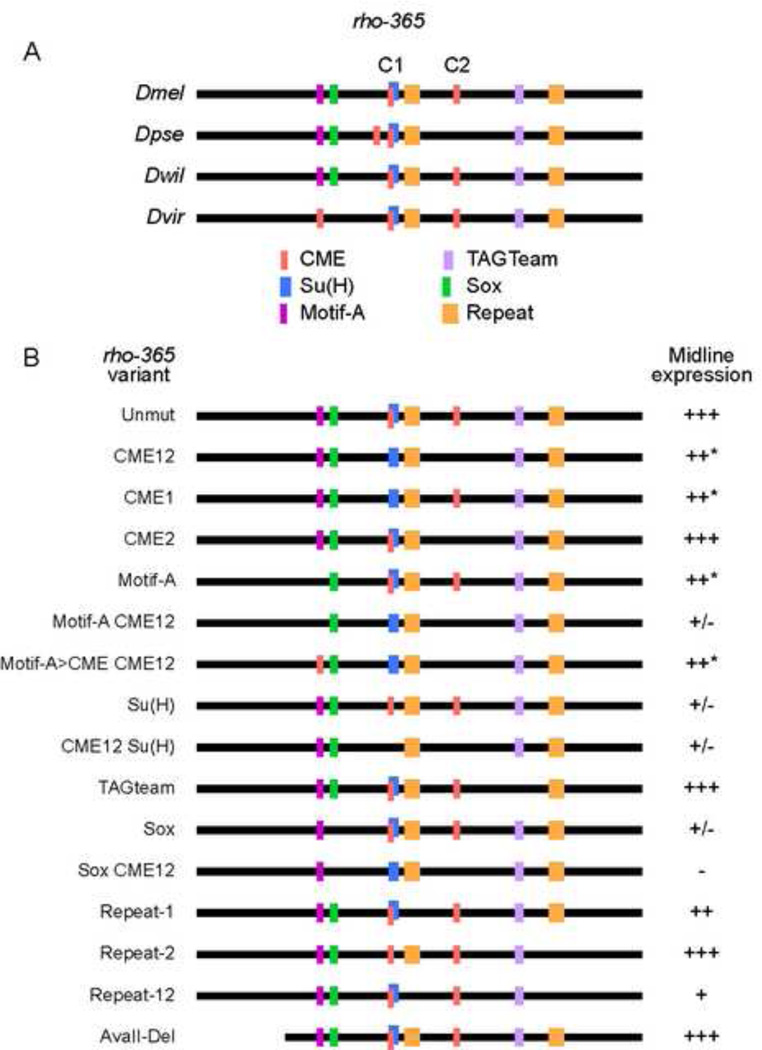
Figure 5. Functional analysis of rho-365 DNA sequence motifs.
(A) Schematic of the rho-365 sequence and representative orthologous sequences among sequenced Drosophila species. Vertically aligned motifs indicate likely orthologous sequences; sequence lines are not drawn to scale. Species shown are: D. melanogaster (Dmel), D. pseudoobscura (Dpse); D. willistoni (Dwil), and D. virilis (Dvir). The two CMEs are indicated by C1 and C2. Note that the first Repeat motif site (orange) in D. willistoni contains a mismatch compared to the D. melanogaster sequence. (B) Mutations were generated in Dmel rho-365 and tested in vivo for midline expression. Absence of a colored block indicates mutation of that sequence; conversion to a different color indicates that the motif was changed to a different motif. Midline expression levels (GFP protein accumulation at s11(m)) were indicated as follows: (+++) normal levels and pattern, (++*) slight reduction in a subset of cells, (++) slightly reduced expression, (+) weak but consistent expression; (+/−) nearly undetectable expression, and (−) no expression.