Figure 7.
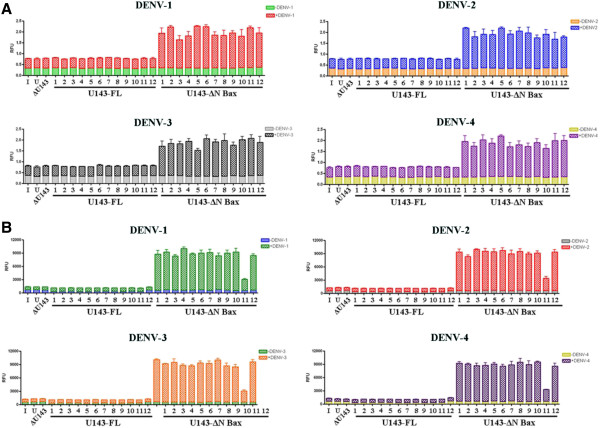
αDENV-U143–ΔN Bax constructs effectively suppress DENV in clonal populations of transformed mosquito cells. A. Clonal cell populations (labeled C-1 through C-11) were challenged with DENV-2 NGC (MOI 0.01). At 4 dpi cell supernatants were collected and saved for RT-PCR analysis. Following DENV-2 E protein antigen staining with antibody, micrographs were taken using the A1-R confocal microscope (Nikon). The figure displayed is an example of what is shown in Additional file 1: Figure S1. Green glowing cells, indicative of positive DENV E-2 staining, were observed only in cells actively replicating DENV. B. RT-PCR analysis of αDENV-U143-FL and αDENV-U143-ΔN Bax clonal cell populations. Supernatants from cell populations were collected prior to antibody staining of cells. RNAs were extracted as described in Methods. RT-PCR amplification was performed with primers to DCA and amplification products were separated on a 2% TAE agarose gel. Control RT-PCR experiments were performed with primers to actin to confirm RNA loading. Heterolgous primers to the intron- ΔN Bax segment of the construct were performed to confirm the presence of our anti-DENV effectors. The approximate sizes (in bases) of the RT-PCR products are indicated. Representative infected cell cultures are shown. C. αDENV-U143–ΔN Bax is capable of full DENV suppression. C6/36 clonal cell populations (designated C-1 through C-12) expressing αDENV-U13-FL or αDENV-U143–ΔN Bax were infected with each of the four DENV serotypes and TCID50-IFA analysis was performed as described in Methods. I-Wt = infected naïve C6/36 cells. I-mCh = DENV infected C6/36 cells transformed with a construct constitutively expressing the mCherry fluorescent marker. U = uninfected naïve C6/36 cells.
