Figure 2. Presynaptic HCN channels and synaptic release in the adult entorhinal cortex (EC).
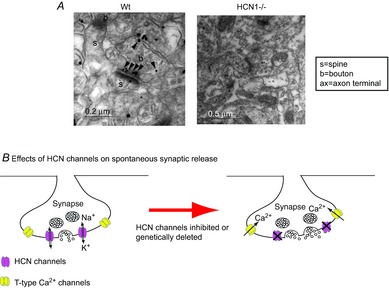
A, immunogold particles for HCN1 in asymmetric synaptic terminals (presumably excitatory glutamatergic synapses) in EC layer III in wild-type (Wt). Labelling was absent in HCN1–/– tissue. Adapted from Huang et al. (2011). B, schematic diagram showing that presynaptic HCN channels and T-type Ca2+ channels are present on the same terminals. Pharmacological inhibition or genetic ablation of HCN1 channels leads to membrane hyperpolarization and enhanced Ca2+ influx through T-type Ca2+ channels, boosting spontaneous synaptic release.
