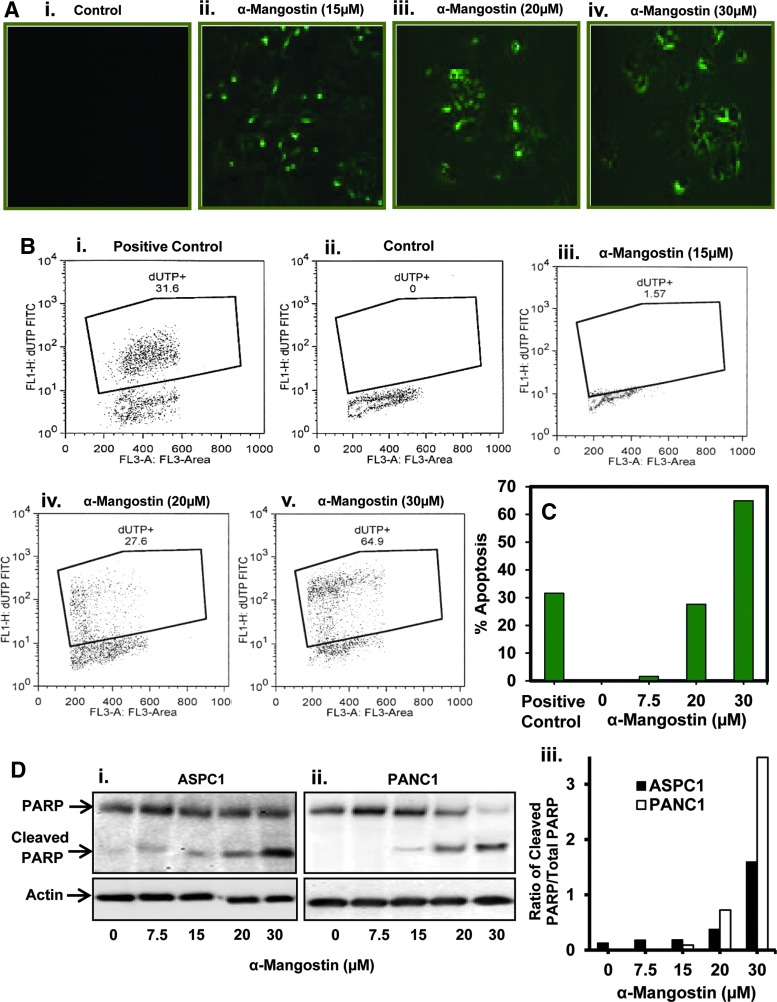
FIG. 2.
Effect of α-mangostin on apoptosis of PC cells. (A) Effect of α-mangostin on apoptosis induction in PC cells as determined by Annexin V staining. Cells were serum starved for overnight and treated with α-mangostin at indicated concentrations for 24 h. α-Mangostin-treated PANC1 cells showing apoptosis as observed by enhanced Annexin V staining (green) by fluorescent microscope. (B) Effect of α-mangostin on apoptosis of ASPC1 cells as assessed by flow cytometry analysis. Cells were serum starved for 24 h and treated with specified concentrations of α-mangostin for 24 h. Induction of apoptosis was quantified by flow cytometry by using APO-DIRECT apoptosis Kit. Representative flow images showing fluorescein-tagged dUTP-nucleotide-labeled cells in positive control cells provided by the kit described previously (Bi), vehicle control (Bii), and α-mangostin-treated (Biii-v) cells. (C) Bar graph represents % apoptotic cells in each group. (D) Effect of α-mangostin on cleaved and total PARP protein levels in PC cells as determined by western blot analysis. Cells were serum starved for 24 h and then treated with the indicated concentrations of α-mangostin for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were prepared for the analyses of total PARP and cleavage of PARP protein levels (Di, ii). Quantitative analysis of total and cleaved PARP proteins (Diii). Bar graph indicates the ratio of total PARP and cleaved PARP proteins. PARP, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase.