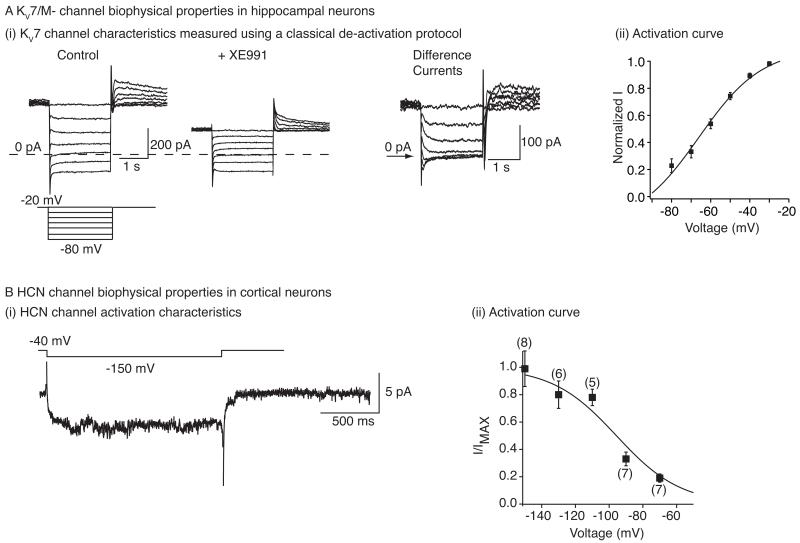
Fig 1. HCN and KV7/M- channel biophysical properties.
A(i) Example recordings of M-current de-activation in hippocampal pyramidal in response to hyperpolarizing potentials from a holding potential of −20 mV. Since there are a number of other conductances also present in these neurons, the recordings were obtained in the absence and presence of the KV7/M- channel inhibitor, XE991 (3 μM). The ‘difference’ current represents the M-current de-activation. (ii) The apparent activation curve of KV7 current produced from experimentally obtained conduction values as detailed in Shah et al. (2008). B(i) Example trace of the HCN channel current recorded from an entorhinal cortical dendrite when it was hyperpolarized to −150 mV from a holding potential of −40 mV. The recording was made in a cell-attached mode. B(ii) The activation curve of Ih obtained using cell-attached recordings made from entorhinal cortical neuron dendrites. A(i) and A(ii) have been adapted from Shah et al. (2008) whereas B(i) and B(ii) have been adapted from Shah et al. (2004).