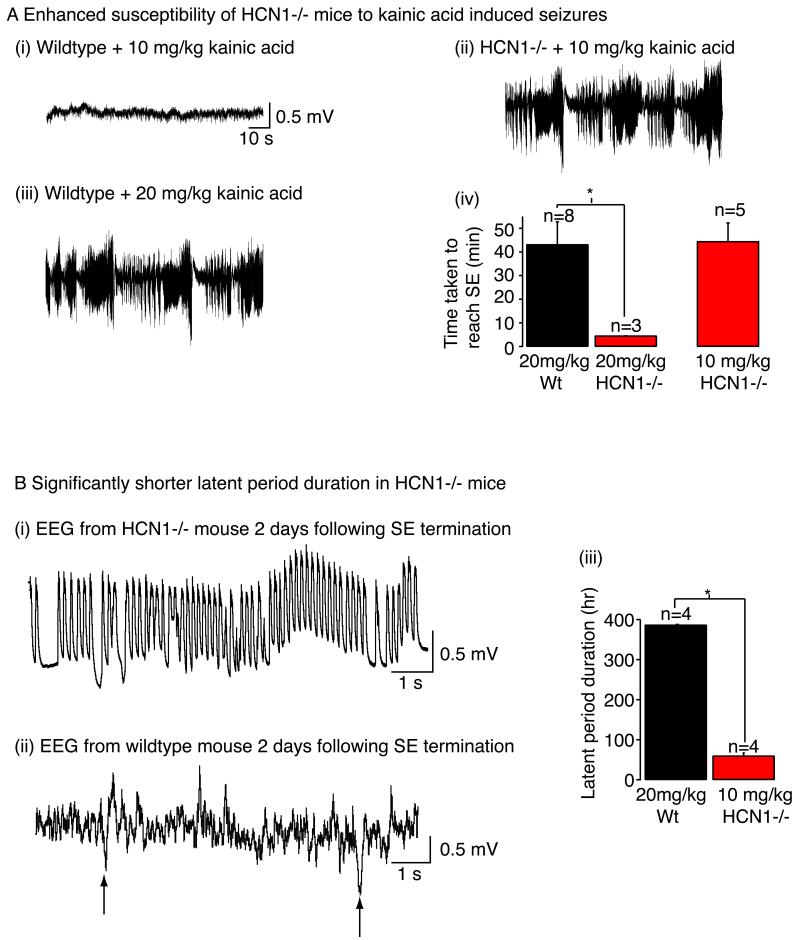
Fig 3. Seizure susceptibility of HCN1 null mice.
A(i), A(ii) and A(iii) Example traces showing the electroencephalography (EEG) recorded from HCN1 null mice and wildtype littermates when administered kainic acid either at concentrations of 10 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg. A(iv) Graph summarising the time taken to induce status epilepticus (SE) with the varying doses of kainic acid. NB Administration of 20 mg/kg kainic acid to HCN1 null mice was lethal whilst treatment with 10 mg/kg kainic acid had little effect on wildtypes for up to 4 hr. B(i) and B(ii) EEG recordings from HCN1 null and wildtype mice 2 days following termination of SE induced with 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg kainic acid respectively. The arrows in B(ii) mark the presence of interictal spikes B(iii) Graph showing the latent period duration (i.e. the time between termination of SE and detection of the first spontaneous seizure) in HCN1 null and wildtype mice when treated with kainic acid. The figure has been adapted from (Huang, Walker et al. 2009).