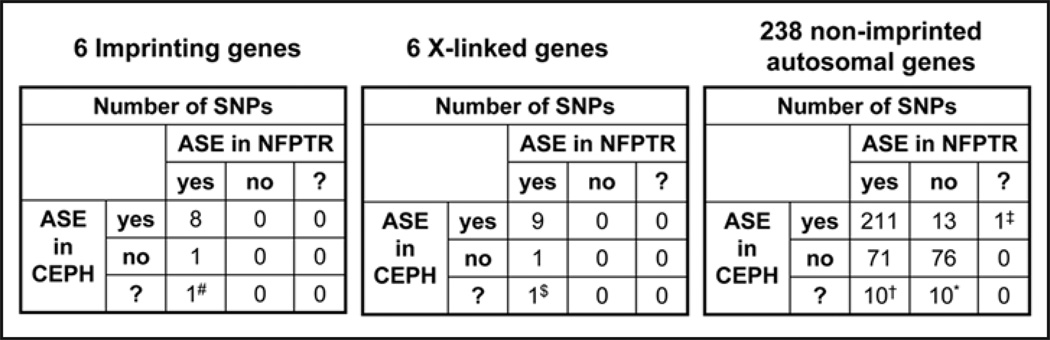
Figure 4.
The extent of ASE in human samples. A total of 413 SNPs in 250 genes were tested for ASE with distributions in control (CEPH) and familial pancreatic cancer (NFPTR) samples as shown. Also indicated are the distributions of 10 SNPs in 6 known imprinted and 11 SNPs in 6 X-linked genes tested; the results on all other genes are shown separately. The yes/no/? categories refer to heterozygotes showing ASE, heterozygotes not showing ASE or the absence of heterozygotes, respectively. #ATP10A (rs3816800) had no CEPH heterozygote. $GUCY2F (rs494589) had no CEPH heterozygote. ‡Ten genes with ASE in NFPTR had no CEPH heterozygotes in our sample. These genes, and their SNPs, are: CCR5 (rs1800023), EPHA1 (rs10952549), EPHA7 (rs7349683), FGFR2 (rs1801043), MAPK4 (rs3288), MMP1 (rs5854), MMP10 (rs470168), RIPK4 (rs3746893), SLC22A2 (rs3127594) and TEK (rs639225). ‡CDH17 (SNP rs9417) had no NFPTR heterozygote. *Seven genes with no ASE in NFPTR had no CEPH heterozygotes in our sample. These genes, and their SNPs, are: AGTR1 (rs5182), CSF1R (rs216123), MMP8 (rs1940475), NAT2 (rs1208, rs1799929, rs1799930), ROS1 (rs529038), THBS1 (rs2228263) and TNFSF8 (rs3181368).