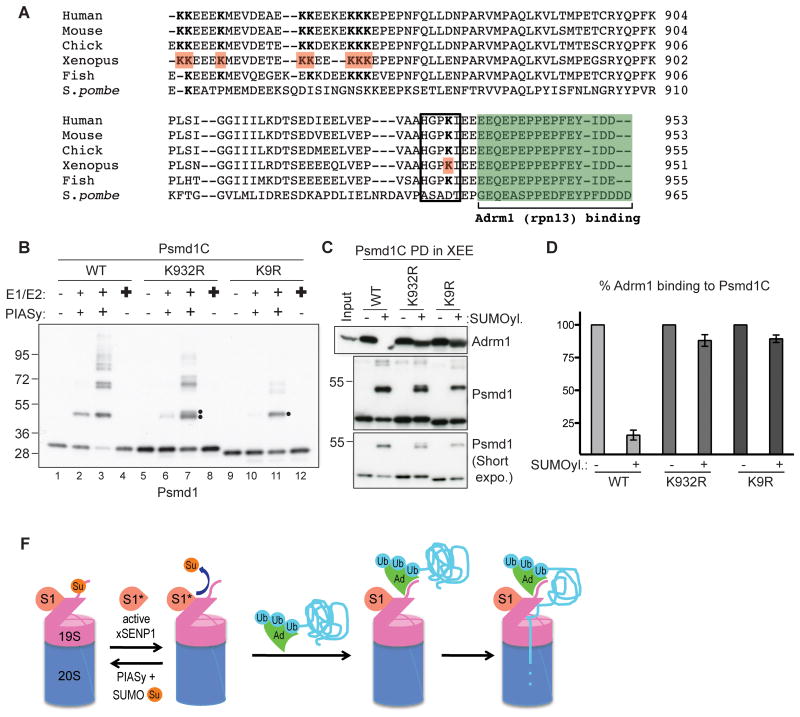
Figure 4. SUMOylation on Lys 932 of Psmd1 is critical to inhibit Adrm1 binding.
(A) C-terminal sequences of human, mouse, chicken, frog, fish and yeast Psmd1 protein, aligned using ClustalW2 program. The green box indicates Adrm1-binding motif. Lysines identified as SUMO acceptors in X. laevis are in red and bold. The black box shows a SUMOylation consensus motif. Note that SUMO acceptor lysines are conserved among higher eukaryotes.
(B) Psmd1C wild type (WT), K932R, and K9R were subjected to in vitro reactions that contain various concentrations of SUMO E1, E2, PIASy. Small “+”reactions contain enzyme concentrations similar to XEE endogenous levels: 15 nM E1, 30 nM E2 and 10 nM PIASy. Medium “+” reactions contain double the level of SUMO enzymes. Bold “+” reactions contain 150 nM E1 and 300 nM E2, but no PIASy. Note that PIASy is essential for Psmd1C SUMOylation. The double dot indicates alternatively SUMOylated forms. The single dot indicates residually SUMOylated forms of Psmd1C observed after nine lysines were mutated to arginine.
(C) Psmd1C WT and mutants treated as in Panel B, under conditions without (lanes 1, 5, 9) or with SUMOylation (lanes 3, 7, 11), were used for pull down assays in XEE. Bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Adrm1 and anti-Psmd1. Input: 5%
(D) Two independent experiments performed as in (C) were quantified using ImageJ. The graph shows Adrm1 levels bound to SUMOylated Psmd1C WT or mutants normalized to Adrm1 bound to the same forms of Psmd1 without prior SUMOylation. Error bar shows standard deviation.
(F) Model: PIASy conjugates SUMO2/3 (Su) to the C-terminus of Psmd1 (extension from 19S-RP), occluding the Adrm1 (Ad) docking site. Active xSENP1 (S1*) antagonizes this modification, allowing Adrm1 recruitment. The balance of conjugation and deconjugation might be regulated, perhaps through conversion of xSENP1 between inactive (S1) and active forms, with deconjugation favoring proteasome activity. Ub: ubiquitinated targets of Adrm1.